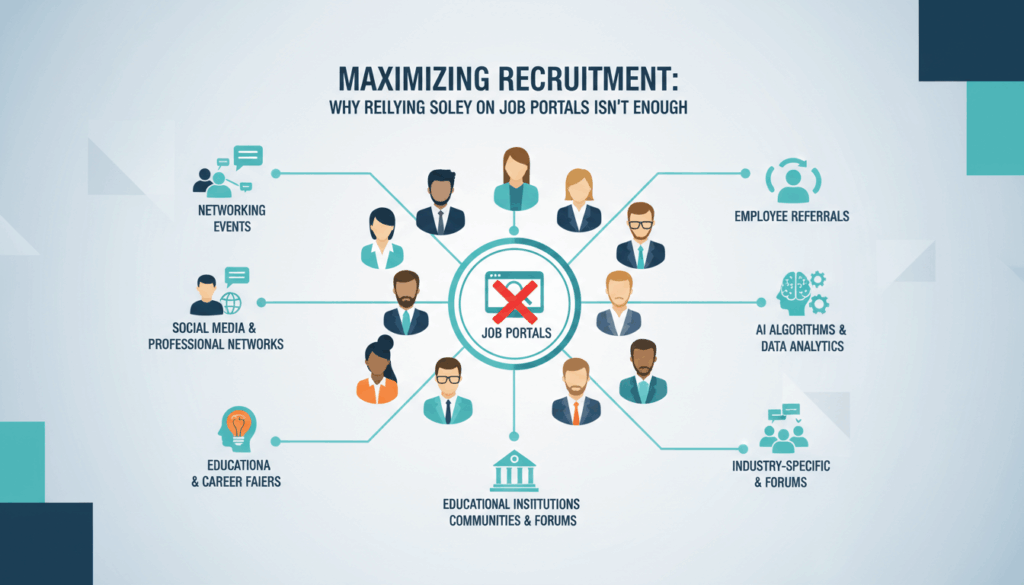
The Limitations of Relying Solely on Job Portals
Relying solely on job portals for recruitment can lead to several challenges that may hinder the efficiency and success of the hiring process. While job portals provide access to a large pool of potential candidates, they also come with inherent limitations that make them insufficient as the sole recruitment strategy.
One significant limitation is the sheer volume of applications that can result from posting a vacancy on popular job portals. This influx can overwhelm hiring managers, making it difficult to efficiently sort through applicants to identify truly qualified individuals. Automated filtering tools often miss nuanced skills and experiences that could be crucial to the role, as these systems generally rely on specific keywords. Consequently, qualified candidates may be inadvertently overlooked.
Moreover, job portals tend to attract passive candidates rather than active talent seekers. Many highly qualified professionals, especially those who are already employed and satisfied with their current roles, may not actively browse job portals. This means that companies might miss out on top-tier talent who could be enticed by a more personalized approach.
Another issue is the generic nature of many job listings on portals, which might fail to capture the unique culture and appeal of a company. Job descriptions often become repetitive as companies template their postings to save time, leading to a lack of engagement from potential job seekers who might not perceive a genuine match between their values and the company’s ethos. Crafting postings that communicate the company’s unique value proposition and culture is vital, yet challenging to achieve on standardized job portals.
Diversity and inclusion priorities may also be compromised when using job portals exclusively. Algorithms and human biases can influence which candidates are seen and selected, potentially perpetuating imbalances rather than correcting them. For example, some filter settings may inadvertently screen out candidates from non-traditional backgrounds who could bring innovation and diverse perspectives to the team.
Additionally, excessive reliance on job portals can bypass valuable recruitment channels such as employee referrals, professional networks, and industry-specific platforms. Referrals and networks often lead to higher-quality hires as candidates are typically pre-vetted by trusted sources. Diversifying recruitment methods to include these channels can enhance candidate quality and increase chances of finding well-suited individuals.
Finally, exclusive dependency on job portals might make a company appear less approachable or flexible to candidates. Personal engagement and networking are increasingly significant to modern recruitment strategies. By reaching out through direct contact, career events, or social media, companies can cultivate relationships with candidates, creating a more dynamic interaction beyond the confines of traditional job listings.
In sum, while job portals are a valuable tool in the recruitment toolbox, their limitations necessitate a more holistic approach to ensure a comprehensive and effective hiring strategy.
Leveraging Employee Referral Programs for Quality Hires
Employee referral programs are a strategic asset in the recruitment toolkit that can elevate the quality of hires. These programs leverage existing employees to identify and recommend potential candidates from within their personal and professional networks. The effectiveness of employee referrals is tied to their ability to produce candidates who are pre-vetted based on both skill and cultural fit, as employees are more likely to recommend individuals they believe will excel in the company environment.
One core advantage of leveraging employee referral programs is the enhancement in candidate quality. Referred candidates often have a deeper understanding of the company culture and expectations from the outset, as explained through the lens of the referring employee. This initial familiarity can result in quicker adaptation and higher retention rates. According to industry surveys, referred employees tend to stay longer at organizations, reducing turnover costs and long-term recruitment needs.
Creating a successful employee referral program involves several critical steps. First, establishing clear guidelines and communication channels is essential. Employees should be well-informed about the types of roles that the company aims to fill and the attributes sought in candidates. This includes sharing detailed job descriptions and aligning them with the company’s strategic goals and cultural values.
Second, incentivizing employees can significantly boost participation in referral programs. This can be achieved through financial rewards, recognition programs, or other non-monetary incentives such as extra vacation days or gift cards. These incentives not only motivate employees to participate but also convey that the company values their input in the hiring process.
Moreover, tracking and feedback mechanisms are crucial for maintaining the efficiency of referral programs. Implementing a system to track the progress and success rate of referred candidates enables a company to identify which employees are most active or successful in bringing in quality hires. Periodic feedback loops, where employees are informed about the outcomes of their referrals, can increase engagement and trust in the system.
In particular, referral programs can support diversity goals by encouraging employees from varied backgrounds to bring in a diverse set of candidates. To optimize for inclusivity, organizations can establish specific diversity-focused referral drives, where employees are encouraged to broaden their networking outreach. This approach can help ensure a more varied candidate pool, enhancing the diversity profile and innovation capacity of the workforce.
Organizations can further support referral programs by integrating them with social media and networking platforms. Encouraging employees to leverage their LinkedIn networks, for example, extends the reach of the referral program beyond immediate personal contacts and taps into a global pool of talent. Employees can act as brand ambassadors, showcasing not only job opportunities but also the company culture and values through their online presence.
Through these strategic implementations, employee referral programs do not merely fill existing roles but bolster the organization with talent that is both qualified and culturally aligned. By integrating such programs into the broader recruitment strategy—complementing rather than solely relying on job portals—companies can ensure a robust and dynamic hiring process that adapts to evolving needs and landscapes.
Engaging Passive Candidates Through Social Media Outreach
In the competitive landscape of recruitment, social media has emerged as a powerful tool to engage passive candidates—those who are not actively seeking new opportunities but may be open to the right proposition. This approach bridges the gap between traditional recruitment methods and the need to reach a broader and more dynamic candidate base.
Passive candidates are often highly skilled professionals who are satisfied in their current roles but could be enticed by attractive opportunities. Leveraging social media effectively to engage such individuals requires a strategic blend of branding, communication, and personalization.
To begin, companies must establish a strong employer brand presence across various social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. This presence should reflect the company’s culture, values, and career opportunities. Creating and sharing engaging content that highlights corporate culture, employee testimonials, and behind-the-scenes glimpses of daily life at the company can build an appealing image that attracts passive candidates.
Sharing value-driven content is crucial. Companies should post articles, industry insights, and other informative content related to their field. This establishes the company as a thought leader and helps in building trust with potential candidates, who see the organization as knowledgeable and influential in the industry.
Engaging passive candidates through social media requires a personalized approach. Recruiters should make use of social media tools and analytics to identify potential candidates whose skills and experiences align with the company’s values and needs. Personalized messages that acknowledge a candidate’s professional achievements or interests can significantly increase response rates. For instance, instead of sending a generic note, a recruiter might say, “I came across your recent project on X and was impressed by your work. We have similar projects here at Company Y and would love to have someone with your expertise join our team.”
Interactive content can also foster engagement. Hosting webinars, live Q&A sessions, or creating interactive polls can attract passive candidates to engage with the company on a deeper level. These events should be promoted through social media to ensure maximum reach and participation. Offering insights into career growth opportunities during these interactions can spark interest from those who aren’t actively looking but are curious about potential career advancements.
Furthermore, leveraging employee advocacy on social media can extend outreach efforts. Encouraging employees to share company posts and create their own positive content about working at the organization can amplify the company’s reach organically. Employees acting as brand advocates often appear more relatable and trustworthy, providing an authentic voice that resonates with potential candidates.
Monitoring social media engagement is key to understanding what resonates with passive candidates. Utilizing analytics tools to track the performance of posts, engagement levels, and audience demographics can offer valuable insights into how well a strategy is working and where adjustments are needed for greater impact.
By carefully crafting a social media strategy that combines consistent branding, personalized outreach, interactive content, and employee advocacy, companies can effectively engage passive candidates. This approach not only broadens the talent pool but also builds a robust pipeline of potential hires who align with the company’s strategic goals and culture.
Building Talent Pipelines via Educational Partnerships
Building partnerships with educational institutions is a powerful way to create robust talent pipelines, providing businesses access to a pool of fresh and innovative talent. These collaborations can be mutually beneficial, offering educational institutions industry insights while furnishing companies with potential candidates who are well-prepared and culturally aligned.
Establishing such partnerships begins with identifying educational institutions that align with your industry or the roles your organization frequently hires for. This allows companies to tap into programs and departments that are directly related to their field, ensuring a better match in terms of skills and knowledge. Engaging with local colleges, universities, and technical schools is key to fostering these connections, as they often house a wealth of potential talent eager to enter the workforce.
One effective approach is developing internship and co-op programs. These programs provide students with practical, hands-on experience in their chosen field while allowing companies to mentor and assess the capabilities of potential future employees. To establish these programs, businesses should work closely with educational institution career services to design meaningful and challenging roles that align with both academic and business objectives. By doing so, companies are not only contributing to the education of students but also grooming talent that is highly familiar with their operations and culture.
Another strategic initiative involves sponsoring student projects or offering guest lectures. By providing real-world challenges for academic projects or sharing industry knowledge through guest speaking engagements, companies can directly influence curriculum development and sharpen students’ focus on skills and technologies relevant to the business world. This engagement helps students gain insights into industry trends and expectations, which better prepares them for employment upon graduation.
Collaborating on research activities can also be highly advantageous. Businesses can partner with faculty and students on applied research projects that align with their strategic goals. This not only supports innovation but also often results in the development of cutting-edge technologies and solutions that benefit both the industry and academia. Such collaboration facilitates a symbiotic relationship where both parties stand to gain from pioneering research efforts.
Scholarship programs targeted at students in areas critical to business needs can also attract top talent. By offering financial support and engaging closely with recipients through mentorships or guaranteed interview opportunities, companies can ensure they attract highly motivated individuals who appreciate the opportunity to develop their careers with supportive employers from the outset.
Moreover, engaging with alumni networks can be particularly useful. Alumni who have graduated and moved into industry roles serve as effective ambassadors for organizations, advocating for job opportunities and offering insights into what makes a company an employer of choice. Businesses can invite alumni to speak at career fairs or participate in panel discussions, further intertwining educational initiatives with professional growth opportunities.
Ultimately, educational partnerships equip companies with access to dedicated, well-prepared candidates who are ready to contribute and innovate. These relationships should be nurturing and ongoing, adapting to industry changes to remain beneficial. By investing in the educational journey of future professionals, businesses take a proactive role in talent development, ensuring a continuous influx of capable, passionate individuals ready to drive success.
Utilizing Niche Platforms and Communities for Specialized Roles
In the recruitment landscape, leveraging niche platforms and communities can greatly enhance the process of filling specialized roles. These platforms cater to specific industries, skills, or professional groups, offering a targeted environment for both employers and candidates.
One of the first steps in utilizing niche platforms is identifying which platforms best align with the roles you are hiring for. For instance, GitHub and Stack Overflow are invaluable for recruiting technical talent such as developers or programmers. These platforms enable recruiters to evaluate the problem-solving skills and coding expertise of potential candidates by reviewing their contributions and interactions. Similarly, for creative roles, platforms like Behance and Dribbble are popular among designers and illustrators, offering a space where candidates showcase their portfolios and previous projects.
Diving into industry-specific communities also offers significant advantages. For example, academic and scientific roles can often benefit from platforms like ResearchGate, where researchers post papers and collaborate on scientific projects. Engaging with these communities can help identify thought leaders and innovators who might not be actively seeking jobs but have valuable insights and skills.
Another approach involves participating in specialized forums and discussion groups. These communities often gather professionals who are deeply engaged with their field, sharing knowledge and insights. For roles in cybersecurity, for instance, engaging in forums like the Cyber Security Forum Initiative (CSFI) or similar communities can provide access to highly skilled professionals. Networking within these forums not only helps identify potential candidates but also builds a recruiter’s brand as a knowledgeable and engaged participant in the field.
To maximize the potential of these platforms, active participation is key. Simply posting job listings may not be sufficient. Recruiters should engage with candidates by contributing to discussions or hosting webinars and workshops on these platforms. This not only increases visibility but also demonstrates commitment and expertise to the community, elevating the employer brand.
Creating partnerships within these platforms can be beneficial. For instance, offering sponsorships for events or competitions within these communities can position a company as a leader in the industry. Aligning with educational or certification initiatives can further enhance a company’s reputation and attract top-tier talent interested in continuous development.
Moreover, companies should encourage their current employees to engage in these communities, acting as brand ambassadors. Employees can share positive experiences and reflect company culture, providing an authentic voice that resonates within specialized communities.
Analytics and tracking tools available on niche platforms can help refine your approach. Monitoring engagement metrics can provide insights into which aspects of the outreach strategy are most effective, allowing for continuous improvement. By assessing which types of content and interactions garner the most interest, organizations can tailor their strategies to better attract suitable candidates.
In summary, utilizing niche platforms and communities involves more than simply posting job listings. By actively engaging and participating in these specialized arenas, companies can access highly skilled and motivated candidates who are aligned with the specific needs of the roles being recruited for. This targeted approach facilitates better matches, improving both hiring efficiency and employee retention. By embedding themselves within these communities, recruiters not only enhance their reach but also bolster their credibility within niche fields.