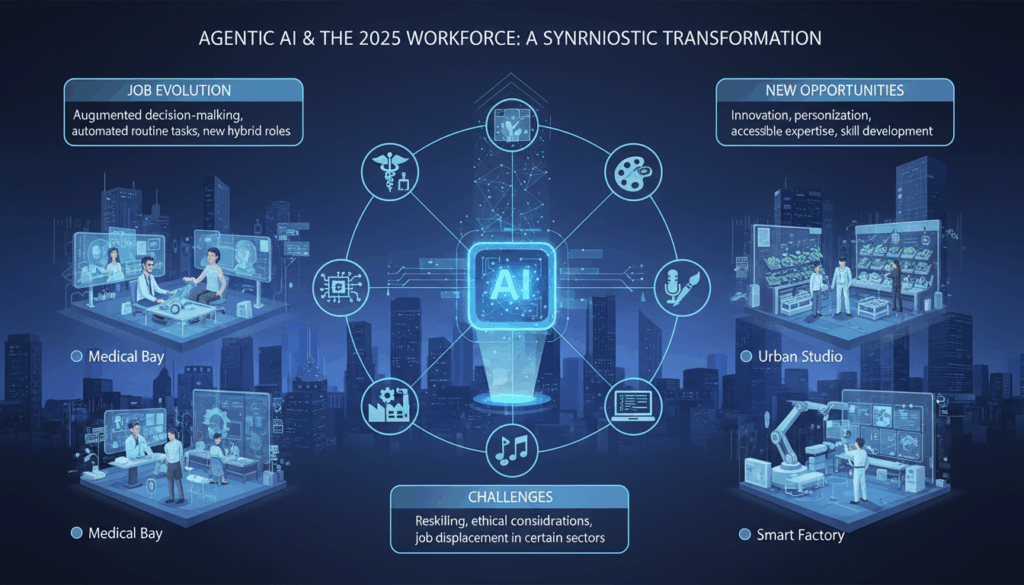
Understanding Agentic AI: Definition and Capabilities
In recent years, there has been a significant push towards understanding artificial intelligence and its various forms. One fascinating branch of AI that has gained attention is agentic AI, characterized by its ability to perform tasks independently while exhibiting goal-directed behaviors. This transformative technology stands apart by emulating a level of autonomy usually associated with human decision-making.
To grasp the essence of agentic AI, it’s crucial first to delve into its definition. Agentic AI refers to systems that are not just reactive, but proactive, enabling them to operate without continuous human intervention. Unlike traditional AI models, which require specific programming for every possible scenario, agentic AI evolves through learning and interaction. This includes gathering information from its environment, making strategic decisions, and pursuing objectives that align with its designed framework.
Agentic AI systems are designed with built-in capabilities that allow for dynamic adaptation. This adaptability is achieved through advanced algorithms within machine learning and deep learning spectrums. Such systems can recognize patterns, understand context, and apply reasoning to make informed decisions. For example, supply chain management systems powered by agentic AI can autonomously optimize logistics operations by continuously analyzing data on inventory levels, delivery schedules, and potential disruptions.
One of the profound capabilities of agentic AI is its inherent ability to learn from feedback and experience. This capability is particularly valuable in complex environments where scenarios change rapidly. Take, for instance, autonomous driving technologies. These systems must interpret vast amounts of sensory information from their environment in real-time, accounting for varying traffic conditions, weather changes, and unexpected pedestrian movements. Agentic AI leverages past experiences and predictive modeling to safely navigate these challenges.
Another key aspect of agentic AI is its capability to collaborate with humans by enhancing cognitive processes. AI-driven personal assistants—like those used in customer service chatbots—exhibit the ability to understand and process natural language, enabling them to hold meaningful conversations, answer queries, and troubleshoot common problems. This capability not only increases efficiency but also personalizes the user experience by adapting to individual preferences and histories.
In the realm of healthcare, agentic AI is revolutionizing diagnosis and treatment processes. AI models trained with vast datasets on various medical conditions can assist doctors by recommending treatment plans tailored to a patient’s unique genetic profile and medical history. This reduces the time needed for diagnosis and allows for more precise and effective patient care.
Moreover, agentic AI has a substantial impact on creative industries. Here, AI systems can generate original content—be it writing, music, or visual arts—by analyzing existing works and synthesizing new ones that satisfy specific themes or styles. This ability not only supports human creators but also expands the boundaries of creativity.
The emergence of agentic AI marks a shift towards systems capable of self-improvement and sustained performance over time. As industries continue to harness these capabilities, the potential for increased efficiency, innovation, and collaboration between machines and humans only grows. This, however, also raises considerations regarding ethical parameters and governance frameworks to ensure that AI technologies are developed and applied in ways that are beneficial to society as a whole.
The Evolution of Agentic AI in the Workplace
The introduction of agentic AI into the workplace represents a paradigm shift in how businesses operate and innovate. Historically, workplace automation has focused on repetitive tasks easily articulated by explicit instructions. However, agentic AI transcends past automation by introducing systems that can autonomously adapt to new contexts, learn over time, and make decisions that traditionally required human judgment.
One of the primary evolutions in the workplace is the integration of agentic AI in decision-making processes. These AI systems can analyze vast datasets to uncover insights and suggest strategies, allowing for more informed and effective decision-making. In industries like finance, agentic AI analyzes market trends in real-time, providing traders and analysts with up-to-the-minute information to make strategic decisions. This real-time data aggregation and interpretation capability helps organizations stay agile in rapidly changing markets.
Additionally, agentic AI’s role in predictive maintenance is transforming industries reliant on heavy machinery and extensive infrastructure. AI-powered systems can anticipate equipment failures before they occur, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs. For example, in aerospace, where safety and operational efficiency are paramount, agentic AI examines sensor data from aircraft to predict when parts are likely to fail and prompt timely maintenance interventions.
In sectors such as retail, agentic AI drives personalization and empowerment in customer interactions. AI systems manage inventories precisely by predicting consumer behavior and optimizing stock levels to meet demands efficiently. Personalization engines, powered by agentic AI, analyze customer preferences and purchasing history to customize the shopping experience, from product recommendations to tailored ad campaigns.
The workforce is also witnessing a significant transformation as agentic AI augments human abilities. In creative fields, designers and writers leverage AI tools that can generate ideas or complete sections of content, enhancing creativity and productivity. Such innovations enable professionals to focus on higher-order tasks while AI assists by generating preliminary drafts or analyzing trends that inform creative directions.
Human resources departments have adopted agentic AI to improve recruitment and employee engagement. AI systems screen resumes, identify potential hires more efficiently, and enhance onboarding processes by customizing training experiences based on individual learning patterns. Additionally, AI-driven analytics offer insights into employee satisfaction and retention strategies, ensuring a more engaged and productive workforce.
However, the evolution of agentic AI in the workplace is not without challenges. The autonomy and decision-making abilities of AI necessitate robust ethical frameworks to ensure transparency and accountability. Companies must design AI systems with ethical considerations in mind, implementing safeguards to prevent bias and ensure decisions made by AI systems align with organizational values and societal norms.
Overall, the evolving presence of agentic AI in the workplace is shaping new job roles and creating opportunities for innovation and efficiency. By fostering a collaborative environment between humans and machines, organizations can harness the full potential of AI while navigating the complex dynamics of technology and human interaction.
Transforming Job Roles: Automation and Augmentation
The advent of advanced AI technologies, particularly agentic AI, is ushering in a progressive evolution in job roles across various industries. Automation and augmentation, driven by these intelligent systems, are significantly transforming how tasks are executed and redefining the skills necessary for the future workforce. This transformation is twofold, involving the automation of routine processes and the augmentation of human capabilities.
In the realm of automation, agentic AI facilitates the shift from manual labor to machine-run processes. This is evident in manufacturing sectors where AI-powered robotic systems streamline assembly lines with precision and speed, leading to increased efficiency and reduced human error. For instance, AI-driven machines in automotive factories autonomously handle welding, painting, and quality control functions, significantly decreasing the need for human intervention in hazardous environments.
Administrative roles, traditionally laden with repetitive tasks such as data entry and schedule management, are also being reshaped. Agentic AI systems are now capable of sifting through large volumes of data, classifying information, and even automating scheduling and correspondence tasks. This automation liberates employees from monotonous duties, allowing them to focus on more strategic and creative tasks, thereby improving job satisfaction and productivity.
On the augmentation front, agentic AI acts as a catalyst for enhancing human abilities, making work processes more efficient while expanding creative and analytical capacities. In sectors like healthcare, AI algorithms assist medical professionals in diagnostics and patient management. By analyzing medical records and peer-reviewed studies, AI systems generate predictive insights, offering recommendations for personalized treatment plans that might surpass human cognitive limitations.
Furthermore, in creative disciplines, augmentation through AI is revolutionizing content production. Writers, musicians, and designers are integrating AI tools into their workflow to generate novel ideas, refine creative output, and expand their artistic horizons. AI can produce initial drafts of articles, suggest chord progressions for composers, and even create visual designs based on predefined style parameters, allowing creatives to explore new dimensions while retaining the final editorial control.
The transformation brought about by this symbiosis of automation and augmentation necessitates a re-evaluation of the skills needed in the workforce. There is a growing demand for individuals adept in digital literacy, data analysis, and AI tool development. Consequently, educational and training programs are evolving to equip workers with these essential skills, ensuring a seamless transition to emerging job roles.
However, this transition also presents challenges, particularly in terms of reskilling and potential job displacement. Companies are encouraged to invest in reskilling initiatives that empower employees to leverage augmented technologies effectively. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with AI-driven transitions and thrive in a future where human-AI collaboration is pivotal.
In summary, as agentic AI continues to revolutionize job roles through automation and augmentation, it paves the way for a more dynamic, efficient, and innovative workforce. Embracing these changes thoughtfully will allow organizations and individuals alike to harness the full potential of AI technologies in reshaping the future of work.
Emerging Opportunities: New Roles and Skill Sets
The transformation brought on by agentic AI in the workforce of 2025 is creating new roles and necessitating fresh skill sets, as organizations adapt to technological advancements. As AI technologies integrate more deeply into various sectors, there is a burgeoning need for expertise in areas that bridge the gap between human and machine interaction.
One of the primary emerging roles is that of AI ethics specialists. As companies deploy agentic AI systems, ensuring ethical use becomes paramount. AI ethics specialists collaborate across departments to establish guidelines that ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI operations. They are responsible for auditing AI algorithms for bias, developing ethical AI strategies, and working with legal teams to maintain regulatory compliance. This role requires a strong foundation in ethical theory, data governance, and familiarity with the technical aspects of AI systems.
Data scientists and analysts are witnessing shifts in skill requirements, as they need to handle more sophisticated AI-driven data strategies. The ability to work with large datasets, employing advanced analytics and machine learning techniques, is now more critical than ever. These professionals are expected to generate actionable insights from data that align with business objectives and inform decision-making processes. Beyond technical skills, the capability to communicate complex data effectively to non-technical stakeholders is increasingly valued.
The rise of AI-driven environments is also giving birth to roles focused on human-AI collaboration. Human-AI interaction designers play a crucial role in ensuring AI systems are intuitive and accessible. They focus on designing interfaces and interactions that promote seamless collaboration between users and AI, thereby enhancing productivity and user satisfaction. This entails a deep understanding of user experience (UX) design principles, cognitive psychology, and human-computer interaction.
The demand for AI trainers is growing, driven by the necessity to enhance AI performance by training models with domain-specific knowledge. AI trainers work closely with engineers and domain experts to provide feedback loops crucial for the continuous improvement of AI systems. They often need expertise in machine learning frameworks, natural language processing, and a detailed understanding of the relevant industry or field application.
Moreover, as agentic AI systems perform increasingly complex tasks autonomously, roles such as AI system supervisors or “AI governors” are emerging. These professionals oversee the operation of AI systems, intervening when necessary to ensure that the AI aligns with organizational goals and societal norms. They act as a bridge between technical teams and leadership, advising on strategic AI integrations and troubleshooting.
In the realm of skills, computational thinking and digital literacy are becoming foundational. Professionals are encouraged to develop an understanding of coding, even at a basic level, alongside problem-solving skills that allow them to interact with AI systems effectively. Creativity and emotional intelligence also gain importance as humans are tasked with leveraging AI for innovative problem-solving while maintaining empathy and emotional awareness in human interactions.
Educational institutions and corporate training programs are responding by developing curricula that target these new competencies. From coding boot camps to AI ethics seminars, there is a proliferation of learning opportunities designed to equip current and future employees with skills that meet the demands of AI-enhanced workplaces.
As agentic AI continues to redefine traditional roles, the focus shifts toward blending technological prowess with human ingenuity. The workforce of the future will be characterized by roles that harmonize human creativity with the analytical power of AI, driving us towards new horizons in productivity and innovation.
Preparing for the Future: Strategies for Workforce Adaptation
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, preparing the workforce for future challenges requires a strategic approach that embraces both change and opportunity. Ensuring that employees are equipped to work alongside agentic AI and other emerging technologies involves a multifaceted strategy that includes skills development, organizational adaptation, and the cultivation of a forward-thinking corporate culture.
Adaptive skill acquisition is at the forefront of workforce preparation. As job roles evolve, so too must the skills possessed by employees. One effective strategy is to implement comprehensive training programs that focus on emerging technologies, digital literacy, and data analysis skills. Organizations can establish partnerships with educational institutions to offer certification programs tailored to the needs of various industries, ensuring that the skillsets match the technological demands.
For example, online platforms such as Coursera and edX provide courses on AI, data science, and machine learning, which can be incorporated into company-sponsored professional development plans. By encouraging continuous learning and providing access to these resources, organizations empower their employees to adapt to new tools and technologies efficiently.
Organizational adaptation goes hand in hand with skill development to create a conducive environment for workforce evolution. This involves redesigning job roles to integrate AI technologies more seamlessly and redefine workflows for efficiency and innovation. Companies must foster a culture of agility and openness to change, encouraging experimentation and creativity.
A practical approach is to adopt an agile work framework, enabling teams to remain flexible and responsive to change. Agile methodologies prioritize iterative progress and collaborative problem-solving, aligning with the dynamic nature of modern AI-driven workplaces. Additionally, companies should focus on implementing cross-functional teams where diverse skills converge, promoting innovation through varied perspectives.
Cultural transformation within an organization is pivotal for preparing the workforce. Businesses should cultivate an ethos of lifelong learning and adaptability, which supports not only skill acquisition but also psychological readiness for change. Encouraging a culture of feedback and open communication strengthens the workforce’s capacity to adapt by recognizing achievements and addressing areas for improvement in real-time.
Leadership plays a crucial role in this cultural transformation. Executives and managers must actively participate in training initiatives and model the desired adaptive behaviors. Hosting regular workshops and seminars on topics such as digital transformation and AI ethics fosters a shared understanding of the technological landscape’s impact.
Moreover, strategic foresight is essential for future-proofing the workforce, necessitating an investment in emerging roles that align with technological advances. For instance, predictive workforce planning tools can be employed to anticipate future skill needs. These tools use data-driven insights to inform strategic hiring and training decisions, ensuring the organization’s human resources align with future technological demands.
Collaboration with industry partners and technology providers enhances these strategies, granting businesses access to the latest innovations and allowing employees to stay abreast of cutting-edge developments. Engaging in industry forums and networking opportunities also fosters an exchange of best practices and innovative ideas.
In essence, preparing the workforce for the future involves equipping individuals with versatile skill sets, fostering an adaptive organizational culture, and embracing strategic foresight to navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by agentic AI and technological advancements. By taking proactive measures, organizations can ensure their workforce is not only prepared but poised to thrive in a future defined by rapid innovation and transformation.