Introduction to Generative AI and Its Evolution by 2025
Generative AI stands on the frontier of artificial intelligence technologies, captivating industries with its capability to create new content from data patterns. This technology has evolved dramatically over the past decade, and by 2025, it is poised to revolutionize the way machines interact with human creativity. The roots of generative AI trace back to advancements in machine learning, particularly deep learning, which enable systems to learn from vast datasets and generate innovative outputs that mimic human creativity. These systems can now create music, art, and even written content, often indistinguishable from human-generated material.
Early generative AI systems relied heavily on algorithms such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), which consist of two neural networks—the generator and the discriminator—working in tandem to improve the quality of generated outputs. The generator creates new data instances, while the discriminator evaluates them, providing feedback that guides the generator towards producing more convincing examples. This adversarial training approach has proven highly effective in refining the production of high-quality, realistic data.
The evolution of generative AI is heavily influenced by the increasing availability of computational power and the richness of data it can access. Enhanced hardware capabilities, like GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units), have empowered researchers to handle larger datasets more efficiently, accelerating the training processes of complex models. Additionally, advancements in data collection and storage technology have permitted models to learn from a broader spectrum of data, resulting in more nuanced and sophisticated outputs.
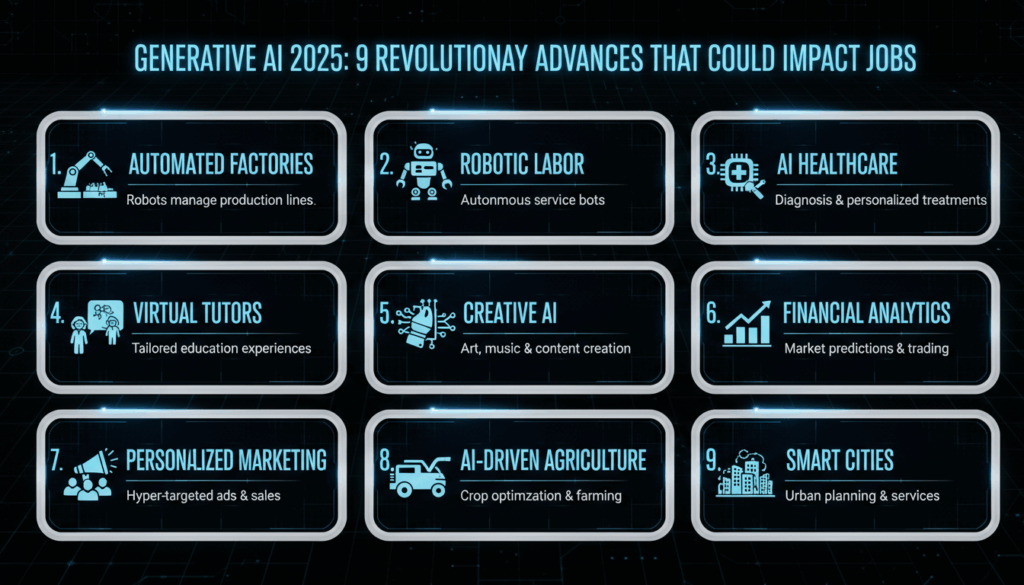
By 2025, generative AI is expected to expand beyond traditional applications, impacting sectors such as healthcare, engineering, and entertainment. In healthcare, for instance, generative models could aid in drug discovery by predicting molecular structures that bind with target proteins, drastically reducing the time and cost involved in bringing new drugs to market. In engineering, AI could assist in designing components by exploring possible configurations far faster than traditional human-led processes.
Moreover, the entertainment industry is burgeoning with creative projects using generative AI, from writing scripts to designing new video game landscapes. These models offer a fresh avenue for creative exploration, allowing designers and creators to push the boundaries of human imagination with the help of powerful computational partners.
Security and ethical considerations will also evolve as generative AI continues its rapid development. As AI systems become increasingly adept at generating content, issues regarding authenticity, intellectual property, and ethical use will become more prominent. It is crucial that frameworks and regulations keep pace with technological advances to ensure these powerful tools are used responsibly.
The trajectory of generative AI suggests that its integration into daily life and professional fields will only deepen, offering profound changes in how we interact with technology and each other. By 2025, the capabilities of generative AI will redefine the boundaries of creativity, providing both challenges and unprecedented opportunities.
Key Advances in Generative AI Technologies in 2025
By 2025, generative AI technologies have reached remarkable advancements, reshaping various industries with transformative capabilities. The increase in both computational power and algorithmic sophistication has led to breakthroughs that are propelling this field to new heights.
One of the most significant advances is in the realm of multimodal AI systems, which can process and generate content across multiple types of data, such as text, images, and audio, simultaneously. These systems aim to unify understanding across modalities, creating outputs that are more coherent and contextually rich. Imagine an AI that can generate a film based on a novel, where scripts, visuals, and soundtracks are all cohesively integrated without distinct human intervention.
Another key development is the refinement of self-supervised learning techniques. Self-supervised models have brought a paradigm shift by minimizing the need for labeled datasets during the training phase. By leveraging vast amounts of data, these algorithms predict parts of data that are hidden from them, teaching themselves the underlying structure without explicit supervisory signals. This has drastically reduced the reliance on human-annotated data, making the training of large-scale generative models more efficient and cost-effective.
Additionally, the emergence of federated learning frameworks has revolutionized how generative models are trained across decentralized data sources. This technology allows models to learn collaboratively without compromising data privacy, aggregating insights from diverse user data to improve model robustness and generalizability. For industries like healthcare, this means creating generative models that can predict patient outcomes with high accuracy while ensuring patient confidentiality.
In the world of creative industries, 2025 has seen the rise of collaborative AI tools that assist humans in real-time creative processes. These tools are designed not to replace human creativity but to act as co-creators that enhance the creative process. For instance, in music production, AI can now suggest melodies, harmonize tracks, and even provide variance to rhythm and tempo, offering composers new dimensions to explore.
Generative AI has also penetrated deeper into the realm of natural language processing (NLP), particularly with the evolution of transformers into even more sophisticated architectures. These advanced models process language with human-like understanding, recognizing context nuances and semantics to generate text that is indistinguishable from human writing. This has broad implications for content generation, customer service automation, and even real-time translation services.
Ethical AI development has gained considerable attention, leading to robust frameworks that guide the responsible application of generative technologies. AI ethics in 2025 emphasize transparency, accountability, and fairness, with extensive research focusing on mitigating bias, ensuring explainability, and protecting against misuse of AI-generated content.
The innovations in generative AI by 2025 showcase a blend of technical ingenuity and interdisciplinary collaboration, driving applications that were previously unimaginable. From enhancing creative processes to redefining data privacy paradigms, these technologies continue to expand the horizons of what AI can achieve.
Impact of Generative AI on Entry-Level and Young Workers
As generative AI continues to evolve and integrate across various industries, it brings profound implications for entry-level and young workers. By 2025, the influence of this technology on the workforce is both a challenge and an opportunity, reshaping job roles, skill requirements, and career paths for new entrants in the labor market.
One of the primary impacts of generative AI is the alteration of traditional job roles, particularly those involving repetitive or standardized tasks. Processes like data entry, basic content creation, and simple analytical tasks are increasingly automated using AI-powered solutions. For instance, entry-level marketing positions that once focused on data collection and basic pattern analysis now benefit from AI tools that automate these tasks, allowing young workers to focus on more strategic and creative aspects. This shift demands a workforce that is adaptable and equipped with critical thinking skills to manage the oversight and refinement of AI outputs.
Generative AI also requires young professionals to develop new skills that align with emerging technologies. Technical proficiency in AI and machine learning principles, even at a foundational level, becomes crucial. Educational institutions and online platforms are increasingly offering courses on AI literacy, enabling young workers to grasp concepts such as neural networks, data ethics, and algorithmic biases. For example, learning how to interact with AI systems effectively, like training neural networks or understanding AI-driven decision-making models, becomes part of standard onboarding processes for many tech-focused companies.
Moreover, generative AI is encouraging a new era of creativity among young workers. The technology allows individuals to build upon AI-generated ideas, enhancing innovation in fields like graphic design, writing, and music production. Entry-level workers can utilize platforms powered by generative AI to experiment with content generation, achieving outcomes previously constrained by time or resources. Imagine a graphic designer using AI to instantly generate multiple creative concepts for a brand campaign, providing a broader framework upon which to infuse personal insights and cultural knowledge.
Furthermore, the presence of generative AI in the workplace necessitates a greater focus on soft skills. While technical acumen is important, skills such as problem-solving, resilience, teamwork, and effective communication are critical. As AI takes over routine tasks, human workers must excel in areas where AI falls short, like empathy-driven customer interactions and nuanced decision-making in ambiguous situations. For instance, customer service roles augmented by AI chatbots still require human agents to handle sensitive scenarios where empathy and understanding surpass programmed responses.
The rise of generative AI also influences the pathways for career advancement. Young workers in tech-savvy environments find themselves rapidly acquiring niche expertise in AI applications, making them highly valuable in emerging roles such as AI trainers, AI auditors, and ethics consultants. Companies are beginning to recognize the potential for cross-disciplinary teams where young workers contribute innovative insights into the development and ethical deployment of AI technologies. This potential not only enhances individual career trajectories but also fosters an environment of continuous learning and adaptation.
Overall, while generative AI poses challenges in terms of job displacement and skill requirements, it also offers unprecedented opportunities for growth, creativity, and innovation for entry-level and young workers. Embracing lifelong learning and adaptability becomes paramount in navigating this new landscape, paving the way for a workforce that is highly skilled and ready to leverage the advantages of generative AI.
Effects on High-Skilled Professions and Knowledge Work
The rise of generative AI by 2025 presents significant shifts in high-skilled professions and knowledge work, fundamentally changing how these workers interact with technology and redefine their roles. Professionals in sectors like law, finance, medicine, and engineering are witnessing AI’s transformative power, leveraging its capabilities for precision, efficiency, and innovation.
In the legal profession, for instance, AI systems are enabling attorneys to conduct legal research with unprecedented speed and accuracy. Advanced AI solutions can analyze vast amounts of legal documents, case law, and statutes to generate insights that were previously time-consuming to uncover. This frees legal professionals to focus on higher-order tasks such as strategic decision-making and offering tailored client advice. Lawyers are increasingly using AI for predictive analytics, assessing the potential outcomes of legal strategies by analyzing historical data and current trends.
In finance, investment analysts and portfolio managers are harnessing AI for complex financial forecasting and risk management. AI-driven tools offer deep insights into market patterns, allowing professionals to anticipate movements and adjust strategies dynamically. The adoption of AI in algorithmic trading has also reduced latency and improved accuracy. Additionally, AI models can detect fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns, protecting both institutions and clientele.
For the medical field, generative AI assists in diagnostics and personalized medicine. It can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, with high precision, often surpassing human capabilities in detecting subtle patterns indicative of disease. Pathologists and radiologists can focus on nuanced judgment that AI cannot replicate, such as considering patient history and integrating novel research findings into diagnosis. Furthermore, AI’s ability to suggest potential treatment plans based on patient data accelerates the move towards personalized healthcare, offering new possibilities in treatment efficacy and patient engagement.
Engineers are utilizing AI for design and development processes that foster innovation and streamline production. AI can simulate myriad design possibilities, rapidly iterating through versions to present optimal solutions. This capability is notably transforming fields like aerospace and automotive engineering, where AI-generated designs are rigorously tested and refined back in the virtual realm before any real-world implementation. The precision and speed of generative AI in simulations empower engineers to focus on creative problem-solving and advanced R&D.
The integration of generative AI enhances collaboration among knowledge workers by automating and optimizing repetitive tasks, allowing for a greater focus on creativity and strategic thinking. For example, content creators and academics use AI to analyze large sets of data quickly, generating insights that can inspire new research directions or creative projects. AI tools enable writers and researchers to draft content faster and provide real-time language and stylistic suggestions, supporting the creative process without overshadowing human input.
Ethical considerations are crucial in the deployment of AI within high-skilled professions. Professionals must remain vigilant about biases in AI algorithms, ensuring that AI outputs serve to enhance, not undermine, their expert decision-making. Transparent AI practices and interdisciplinary collaboration lead to innovative solutions that respect ethical norms and cultural sensitivities.
Thus, the landscape for high-skilled professions and knowledge workers is greatly enriched by the advent of generative AI. Expertise is not replaced but augmented, as professionals evolve to include AI literacy and ethical considerations as integral components of their roles. This symbiotic relationship between AI and human intelligence fosters a future where technology amplifies human potential, unlocking new horizons of creativity and efficiency.
Strategies for Workforce Adaptation and Skill Development
In adapting to the rapid advancements in generative AI technologies by 2025, organizations must implement strategic workforce adaptation and skill development plans to remain competitive. This involves a multi-faceted approach that addresses the continuous evolution of job roles and the emergence of new skills required to harness AI’s potential effectively.
Effective adaptation strategies begin with a robust upskilling and reskilling program. Organizations should identify skill gaps created by generative AI integration and offer targeted training programs to fill these needs. For example, employees previously involved in repetitive data processing might now require training in AI system operations, data interpretation, or AI-enhanced decision-making frameworks. Companies can utilize online platforms offering AI and data literacy courses or partner with educational institutions to provide customized training solutions.
Cross-disciplinary learning is another crucial component. The integration of AI across all areas of a business necessitates a workforce that understands not only their specific roles but also how AI impacts their field. Encouraging employees to understand basic AI principles across finance, marketing, and HR helps build a cohesive understanding of AI’s role within the organization. For instance, marketing teams can learn how AI analyzes consumer behavior to craft strategic campaigns, aligning their skills with AI-driven insights to enhance decision-making.
Implementing mentorship programs that pair employees with AI application experts accelerates the learning curve and fosters a culture of knowledge sharing. Experienced mentors can provide practical insights into AI technologies, helping mentees apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios effectively. This hands-on guidance is pivotal in transitioning from traditional workflows to AI-augmented processes, ensuring employees feel supported during this transition.
To cultivate an innovative mindset, businesses should encourage experimentation with AI tools, creating sandbox environments where employees can safely explore AI capabilities without the risk of failure impacting the business. Pilot projects can be initiated to explore AI applications across various departments, encouraging collaboration and open dialogue about challenges and discoveries. Such initiatives empower employees to contribute creatively to the company’s AI strategy, fostering a sense of ownership and engagement.
Moreover, focusing on the development of soft skills such as adaptability, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence cannot be overlooked. As AI technologies handle more technical tasks, the human element will be key in areas requiring nuanced judgment and complex problem-solving. Training programs that incorporate scenarios for communication, negotiation, and leadership in AI-enhanced settings should be developed to complement technical skills, ensuring that the workforce remains versatile and adaptive.
Finally, companies should establish clear pathways for career progression in the AI era. This involves redefining job roles and creating new career pathways where AI expertise is central. Offering certifications recognizing new skills acquired in AI operations, data management, or ethical AI practices could motivate employees to pursue continuous learning, aligning their growth with the evolving technological landscape.
Through these strategies, organizations not only ensure that their workforce is equipped to handle the challenges brought about by generative AI but also position themselves to take advantage of the opportunities it presents. Building such resilience and adaptability into the workforce ensures a sustainably competitive organization well-prepared for future advancements.