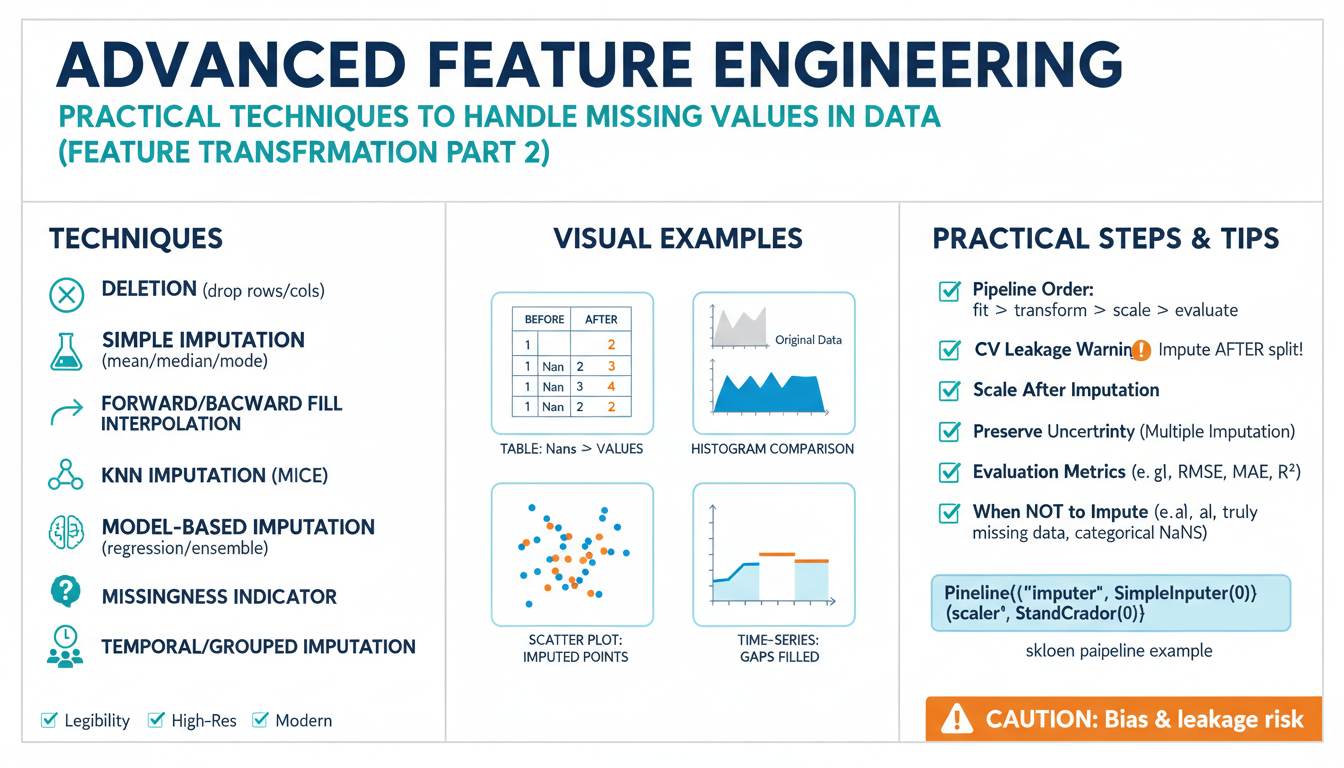
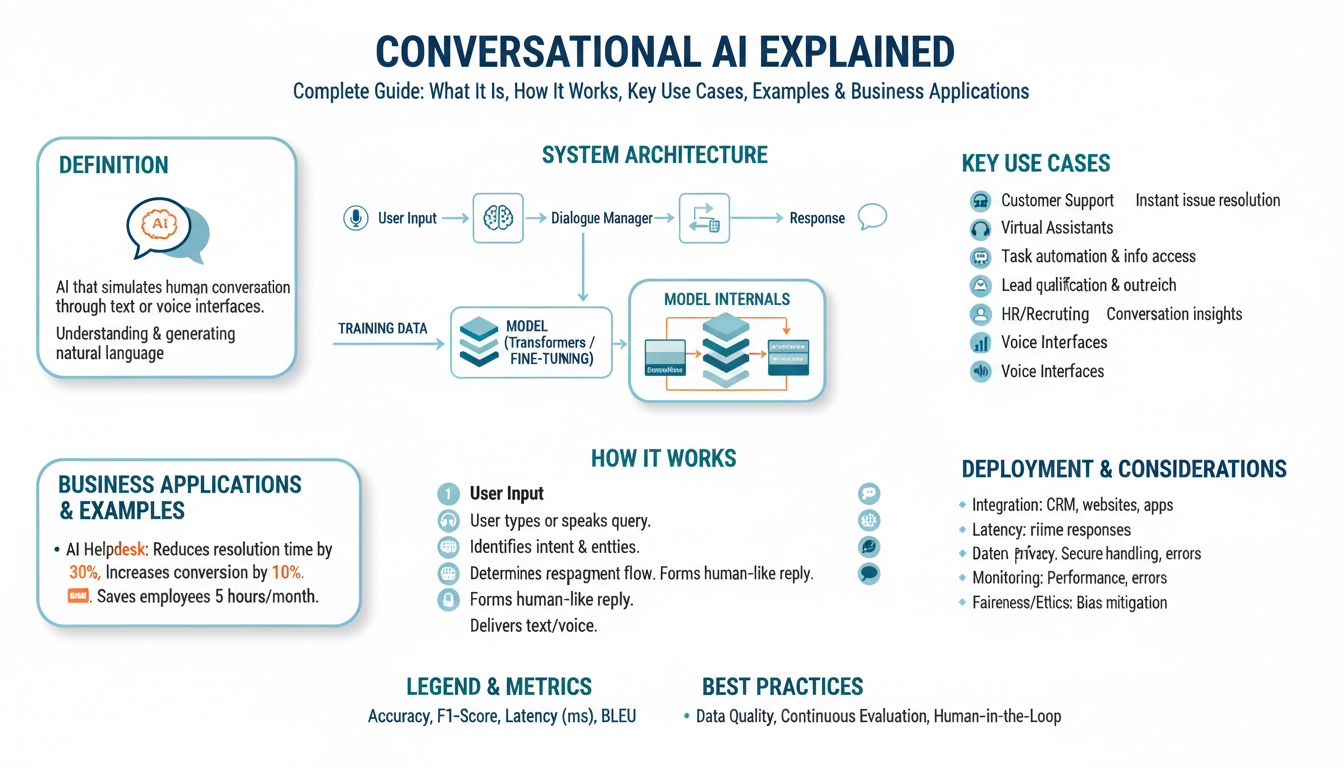
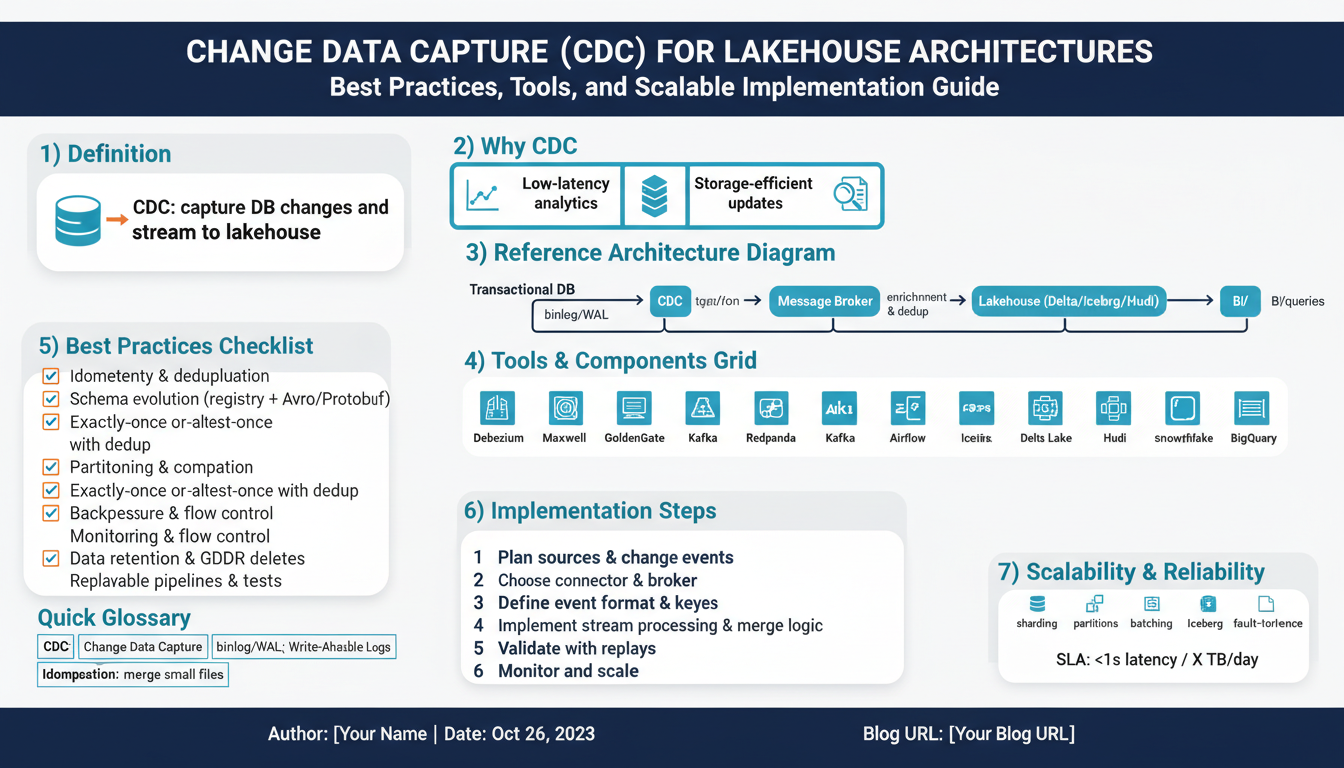
How ChatGPT is Transforming Communication and Productivity
Artificial intelligence has become an integral part of our everyday activities, and ChatGPT is at the forefront of this transformation. By leveraging advanced natural language processing, ChatGPT enhances communication and productivity in ways that were considered futuristic just a few years ago.
One of the most profound impacts of ChatGPT is its ability to streamline and refine communication. Whether you are drafting emails, creating proposals, or collaborating with colleagues across time zones, ChatGPT offers instant feedback and intelligent suggestions, allowing for clearer, more concise correspondence. For example, professionals can use ChatGPT to immediately transform a rough draft into polished, professional messages, saving time and minimizing misunderstandings. According to a study by MIT, AI-powered writing assistants significantly improve efficiency and job satisfaction in knowledge-based industries.
ChatGPT also excels at breaking down language barriers, making global collaboration more feasible than ever. With built-in translation and summarization tools, teams can collaborate across continents without worrying about linguistic discrepancies. These features are especially valuable in multinational companies or academic collaborations, where clear communication is paramount. As reported by Brookings Institution, AI-powered tools like ChatGPT are revolutionizing the way information is processed and shared across various sectors.
From a productivity standpoint, ChatGPT acts as a virtual assistant capable of handling a variety of repetitive tasks. Scheduling meetings, generating reports, and gathering research can all be delegated to the AI, allowing users to focus on higher-level strategic activities. By automating such administrative chores, employees are able to dedicate more energy to creative problem-solving and innovation—a shift supported by Harvard Business Review research on generative AI’s impact on creative work. For instance, marketing professionals use ChatGPT to brainstorm campaign ideas and draft multiple social media posts in a fraction of the time it would normally take.
Additionally, ChatGPT facilitates knowledge management and decision-making. It can quickly analyze large volumes of data, summarize complex documents, and present actionable insights. This data-driven support assists leaders and managers in making informed decisions without spending hours sorting through reports. For example, a project manager can input progress updates, and ChatGPT will synthesize the information into a concise status report, highlighting risks and recommending next steps.
In summary, ChatGPT is not just enhancing communication—it is fundamentally transforming the way we work. By automating routine tasks, breaking down language barriers, and providing intelligent suggestions, ChatGPT empowers individuals and organizations to operate more efficiently than ever before. Its role as a productivity accelerator and communication enhancer is already making waves, leading businesses and individuals alike to rethink their daily workflows.
Key Features and Benefits of ChatGPT
ChatGPT offers a host of features designed to make everyday tasks easier, bridge communication gaps, and enhance productivity across various domains. Whether you’re a student, professional, or casual user, its advanced capabilities deliver substantial benefits. Here’s an in-depth look at its most useful features and the real value it brings to the table:
- Natural Language Understanding
ChatGPT’s strength lies in its ability to understand and generate natural, human-like language. This allows for smooth, intuitive interactions where users can ask questions, provide commands, or have conversations without needing to use technical jargon. For example, instead of writing code, you can ask, “Can you summarize this research article for me?” and receive a concise, readable overview. This technology is grounded in the latest advances in natural language processing (NLP), ensuring impressive accuracy and fluency in responses. - Information Retrieval and Research Support
ChatGPT can assist with summarizing long documents, finding explanations for complex concepts, and even providing citations for academic work. For instance, students can inquire, “What are the key differences between renewable and non-renewable energy sources?” and receive a well-structured, nuanced comparison. Its ability to access and condense vast repositories of information makes it invaluable for research and learning. For a deeper look at AI’s role in education, consider exploring the insights from Stanford University’s education technology research. - Content Generation and Creativity
Creators leverage ChatGPT for brainstorming ideas, drafting blog posts, composing emails, or even writing poetry. By inputting prompts like, “Help me create a catchy headline for a marketing campaign,” users receive imaginative suggestions. This feature democratizes content creation, empowering individuals and small businesses who may not have access to dedicated writing staff. The New York Times discusses how AI’s creative capabilities are reshaping creative industries. - Multilingual Capabilities
ChatGPT isn’t limited to English; it supports multiple languages, making it a powerful tool for users around the globe. You can request translations, ask for help with foreign-language emails, or clarify grammar points in other languages. With rising globalization, this multi-language support is crucial for effective cross-border communication. The European Commission highlights the importance of AI in supporting multilingualism in Europe. - Personalization and Context Sensitivity
One of the standout features is ChatGPT’s ability to maintain context over a conversation, adapting responses to your preferences or requirements. For example, after clarifying that you’re seeking vegan recipes, subsequent queries about meal ideas will stay within that dietary preference. This context retention streamlines interactions, reducing the need to restate information over and over. For more on how context-aware AI is evolving, see this overview from IBM’s AI experts. - Accessibility and Ease of Use
Perhaps the most democratizing benefit is ChatGPT’s accessibility. Whether integrated into a website or accessed via mobile apps, it is always a few clicks away, providing instant support for tasks large and small. From helping non-native speakers draft professional correspondence to assisting visually impaired users through voice-activated chat, AI is a game-changer in inclusive technology. The World Economic Forum explores how AI improves digital access for people with disabilities.
Each of these features not only simplifies tasks but also unlocks new opportunities for creativity, learning, and global collaboration. By blending massive data resources with intuitive design, ChatGPT stands as a versatile assistant for the modern digital era.
Real-World Use Cases for ChatGPT
ChatGPT has garnered significant attention for its versatility in a range of real-world scenarios. Its ability to interpret natural language, synthesize information, and converse fluently makes it a game-changer for both individuals and businesses. Here’s a closer look at some practical applications, illustrated with steps and examples, to highlight where ChatGPT excels and how it adds value:
1. Content Creation and Brainstorming
Writers, marketers, and content creators utilize ChatGPT to overcome creative blocks and speed up idea generation. By inputting prompts like, “Generate ten blog post ideas about renewable energy,” users receive diverse suggestions in seconds. The tool also assists in outlining articles, suggesting catchy headlines, and even drafting social media captions, boosting productivity and creativity. For further insights into how AI tools support content creation, check this Nieman Lab report.
2. Customer Support Automation
Many businesses integrate ChatGPT into their customer service infrastructure to automate responses for common inquiries. For example, an online retailer can deploy a chatbot on its website to instantly answer questions regarding return policies, order tracking, or product specifications. This not only improves response times but also frees up human agents to handle more complex tasks. Case studies from organizations using AI for customer service can be found at Harvard Business Review.
3. Tutoring and Education Support
Educators and students rely on ChatGPT for help with explanations, language practice, and even personalized study recommendations. For instance, a student struggling with algebra can ask, “Explain how to solve quadratic equations,” and receive step-by-step solutions. Teachers might use the tool to draft lesson plans or quizzes. Find more about AI’s impact on education from Education Week.
4. Coding Assistance and Debugging
Programmers leverage ChatGPT to write code snippets, troubleshoot errors, and understand complex programming concepts. By pasting an error message or describing an issue, such as “Why does this Python code give a TypeError?”, users often receive instant explanations and solutions. For examples and tips, refer to research from academic institutions on AI-driven code assistance.
5. Language Translation and Communication
Global teams and travelers use ChatGPT to translate text or clarify language nuances. For everyday communication or understanding foreign-language documents, ChatGPT helps break down barriers. Although not perfect for legal or medical translations, it handles routine conversations adeptly. The Brookings Institution explores how AI is impacting language translation globally.
These use cases demonstrate ChatGPT’s broad applicability and ability to enhance efficiency and creativity across fields. However, it’s essential for users to recognize the need for human oversight, especially in scenarios requiring strict accuracy or nuanced understanding, as explored further in the next sections of this discussion.
Understanding the Limitations of AI Language Models
While ChatGPT and other AI language models have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, it’s essential to recognize their inherent limitations. Understanding these constraints helps users set realistic expectations and utilize AI more effectively.
AI Lacks True Understanding
AI models like ChatGPT generate responses based on patterns in the data they have been trained on, not genuine comprehension. They excel at mimicking human-like text but do not possess consciousness or awareness. For example, while ChatGPT can generate a recipe or answer a historical question, it cannot grasp the deeper meaning behind a philosophical debate. This limitation means AI sometimes produces plausible-sounding yet factually incorrect or nonsensical answers. For an in-depth look at this issue, explore insights from MIT Technology Review.
Knowledge Cutoff and Real-Time Information Gaps
ChatGPT operates based on information available up to its last training data cutoff, which is often months or even years behind the present day. This means it cannot access current events, breaking news, or real-time data. For instance, it cannot provide up-to-the-minute stock prices or details about new scientific discoveries published after its training period. For updated and reliable information, always supplement AI responses with trusted sources like The New York Times or Nature.
Sensitivity to Input and Output Quality
AI-generated content is highly dependent on the phrasing and clarity of the user’s prompt. Vague or ambiguous queries may result in equally unclear or irrelevant answers. Additionally, AI may produce different outputs when asked the same question in various ways. For instance, the specific wording “How does AI impact education?” might yield a general overview, while a more precise prompt such as “List three ways AI is changing classroom teaching methods in 2024” will likely result in a more focused response. For guidance on crafting effective prompts, resources like the Harvard Business Review offer practical advice.
Potential for Bias and Inaccuracy
Language models are trained on vast internet datasets, which inadvertently include biases and inaccuracies present in the source material. As a result, these models may sometimes reproduce or amplify social, cultural, or ideological biases. This can affect the neutrality and reliability of outputs, especially in sensitive topics such as politics, health, or social justice. For additional reading on algorithmic bias, visit the Brookings Institution.
No Personal Experience or Emotional Intelligence
ChatGPT does not possess feelings, beliefs, or personal experiences. This gives it a unique detachment and objectivity but restricts its capacity for genuine empathy or context-based understanding. For example, while ChatGPT can suggest techniques for managing stress, it does not empathize with users’ emotional states the way a human friend or counselor might. Learning more about these distinctions is important—consider reading the American Psychological Association’s analysis of AI in therapeutic settings.
Recognizing these limitations is not a reason to avoid using ChatGPT or similar tools, but a reminder to use them thoughtfully and in combination with critical thinking and human expertise.
Common Misconceptions About ChatGPT’s Abilities
One of the most widespread misconceptions about ChatGPT is the belief that it is an all-knowing, infallible source of information. While the underlying technology is indeed powerful, there are important limitations users should understand to use it effectively.
First, ChatGPT operates based on patterns and knowledge found in large datasets amassed until a certain cut-off date—in most cases, knowledge up to 2024. It does not “know” facts as a human expert does, nor can it access real-time data, breaking news, or personal user information unless those are explicitly shared in the conversation. For example, if you ask ChatGPT about a recent event such as the outcome of a 2024 sporting event, it may not provide accurate or current answers. You can read more about AI training limitations at DeepMind’s overview of training data.
Secondly, many users think ChatGPT has human-like understanding and reasoning. In truth, its responses are generated based on statistical patterns, not true comprehension. This can lead to plausible yet incorrect or misleading answers, commonly known as “AI hallucinations.” For instance, it might generate a fake but realistic-sounding citation or invent a concept when asked for something outside its training. More on this phenomenon is explored by Nature’s article on AI hallucinations.
Another common misconception is that ChatGPT can replace specialized professionals, such as lawyers, medical doctors, or financial advisors. While it can provide general advice or summarize information, it should never substitute for consultations with certified experts. For matters of health, law, or finance, relying solely on an AI’s output can have serious consequences. Major organizations like the American Medical Association offer ongoing guidance on using AI responsibly in professional fields.
Finally, there’s the belief that ChatGPT’s output is unbiased and neutral. In reality, AI models can inadvertently reflect biases present in their training data. As a result, careful human evaluation is essential, especially for sensitive issues. Read more about the complexities of AI bias at IBM’s resource on AI bias.
By understanding these limitations, users can better leverage ChatGPT for what it does best: generating text, summarizing information, and offering creative assistance—while staying critical and verifying important details independently.
Ethical and Practical Considerations When Using ChatGPT
When integrating ChatGPT into your workflows, it’s crucial to weigh both ethical and practical considerations. While AI-powered language models can dramatically enhance productivity, creativity, and access to information, humans remain responsible for how these tools are applied. Here are detailed considerations that must guide responsible usage:
Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability
ChatGPT generates plausible-sounding responses, but it isn’t always correct or up-to-date. Relying blindly on its outputs—especially for medical, legal, or financial advice—can be risky. Users should always fact-check crucial information before acting on it. For example, double-check data using reputable sources such as CDC for health advice or The New York Times for current events.
Ethical Implications and Bias
ChatGPT learns from enormous datasets, much of it scraped from the internet, which means it can inherit and even reinforce biases, stereotypes, or misinformation. Ethical concerns include:
- Bias Reinforcement: Be aware of the model’s potential to perpetuate prejudiced viewpoints. Consider consulting diversity and inclusion resources such as AAAS.
- Plagiarism: Although ChatGPT does not intentionally copy content, its responses may unintentionally echo existing material. Always check for originality, especially when creating educational or public-facing resources.
- Consent and Privacy: Never input sensitive personal information into ChatGPT. OpenAI advises against sharing private data, reflecting data privacy laws like GDPR, which stress users’ right to privacy and data protection.
Transparency and Attribution
When using AI-generated content, it’s best practice to disclose that AI assisted in the creation. This transparency helps maintain trust, especially in educational or public settings. Some academic environments encourage or require explicit citations for AI-generated content; readers can refer to Harvard Library’s guide on citing AI tools.
Human Oversight and Augmentation
Rather than viewing ChatGPT as a complete replacement for expertise, it’s best employed as a tool for augmentation. For example, teachers might use it to draft lesson plans, but should always refine materials based on their own expertise and students’ specific needs. Similarly, content creators can use AI for brainstorming, but final drafts should reflect a human touch. For more on best practices, see this Harvard Business Review article on ethical AI.
Managing Misinformation Risks
Unchecked, AI tools can spread or amplify misinformation. To counter this, always:
- Vet generated information with credible sources (Snopes for fact-checking, for instance).
- Promote digital literacy by training teams and students to critically evaluate AI outputs.
- Encourage a culture where asking for evidence is expected and valued.
By thoughtfully considering these ethical and practical dimensions, users can harness ChatGPT’s potential while minimizing risks and affirming human responsibility in the digital age.