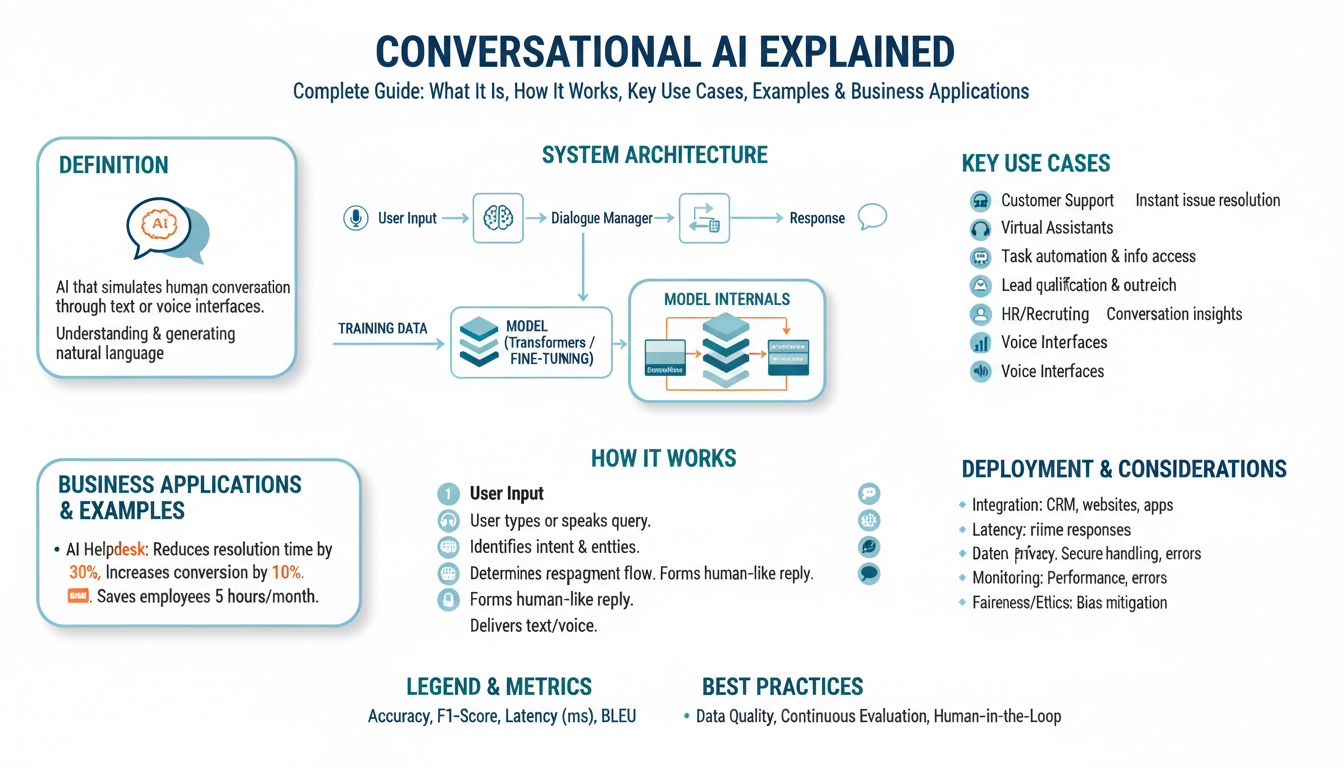
What Is Conversational AI
Conversational AI combines natural language processing (NLP), dialogue management, and often large language models to let systems understand and generate humanlike text or speech. In plain terms, conversational AI is the software stack that turns user utterances into actionable intents and then produces a response that moves a conversation forward. Natural language processing here means everything from tokenization and intent classification to contextual embeddings; calling it out early helps you reason about where errors will surface. If you think of a chatbot as the visible surface, conversational AI is the engine under the hood that makes that surface useful.
The system breaks down into predictable components: input processing (speech-to-text if voice), natural language understanding (NLU), dialogue manager (state and policy), response generation (NLG), and backend integrations. Define NLU as the component that maps user text to intents, entities, and context; define NLG as the component that turns structured outputs into fluent text. Dialogue management tracks conversational state and applies policies—rule-based, learned, or hybrid—to decide next actions, such as querying a database, calling an API, or asking a clarification question. These components compose synchronously or asynchronously depending on latency and throughput needs.
Under the hood you’ll encounter two dominant engineering patterns: retrieval-augmented systems and end-to-end generative systems. Retrieval-augmented approaches use a vector store or knowledge base to fetch relevant documents, then synthesize an answer—this minimizes hallucination when accuracy matters. End-to-end generative systems, often powered by large language models, excel at free-form, empathetic responses but require guardrails for safety and factuality. You’ll commonly combine both: use retrieval for grounding and a generative model for surface fluency, routing ambiguous queries to a human agent when confidence drops.
A practical processing pipeline looks like this in sequence: ingest -> normalize -> classify intent & extract entities -> retrieve context -> apply dialogue policy -> render response -> log for learning. For example, in a support flow you might run intent classification (“refund_request”), extract slots (order_id), call the orders API, and then use a template or model to generate the reply. In code terms, the pattern is often an orchestrator that coordinates microservices (NLU, vector DB, policy engine) and enforces timeouts and fallbacks so the user experience degrades gracefully rather than fails outright.
Real-world use cases reveal different trade-offs. In customer support you prioritize correctness, auditability, and seamless human handoff; in internal developer assistants you prioritize context-window depth and tooling access (repo search, code execution); in voice agents you must optimize ASR accuracy and low-latency response times. For instance, a banking chatbot will restrict generative freedom and prefer deterministic templates for compliance, while a marketing copy assistant can favor creative outputs. Choose architecture and models to match those constraints rather than optimizing for novelty alone.
How do you measure whether a conversational AI implementation works? Track objective metrics (intent accuracy, slot F1, end-to-end task completion rate, mean time to resolution) and subjective signals (CSAT, conversation delight, escalation frequency). Monitor runtime metrics—latency, throughput, and failure rates—and instrument conversation logs for drift so you can retrain NLU models or refresh your retrieval index. Iterate on prompts, policy thresholds, and fallback behaviors using A/B tests and regular human-in-the-loop reviews to keep the assistant aligned with business goals.
Building on this foundation, we’ll next dig into specific model choices and orchestration patterns that scale—how to combine vector search with prompt templates, where to cache context, and which evaluation pipelines prevent regression. That technical detail is where you convert the conceptual components above into resilient production systems that meet both user expectations and operational constraints.
Core Components and Architecture
Building on this foundation, an effective conversational AI architecture stitches NLU, dialogue management, vector search, and response generation into a resilient runtime that meets latency, accuracy, and compliance goals. Start by treating the orchestrator as the single decision point that routes requests between synchronous NLU calls, fast cache lookups, and asynchronous retrieval-augmented workflows; this ensures you can enforce timeouts and fallbacks consistently across the stack. We emphasize vector search and grounding early in the request path so the generative model receives verified context rather than raw, untrusted documents. Designing with these priorities reduces hallucination risk and keeps dialogue management auditable.
Separate the control plane (orchestrator, policy engine) from the data plane (NLU models, vector DB, business APIs) so you can scale each independently and upgrade models without touching routing logic. In practice we implement the orchestrator as a lightweight microservice that performs callNLU(), then fetchVectors() when intent requires knowledge, and finally applyPolicy() to decide whether to call an LLM, a template renderer, or a human agent. Use circuit breakers and adaptive timeouts: if vector search exceeds latency budget, fallback to cached summaries or deterministic templates. This pattern gives you predictable latency and graceful degradation under load.
Manage conversational state across two tiers: ephemeral session state in a low-latency store (for example Redis) and canonical, long-term context in a vector database or document store. Store short-lived slots, turn history, and policy variables in the session cache for quick access; persist embeddings and conversation summaries to the vector DB to maintain recall across sessions. We recommend sliding-window summarization to keep context within model token limits—summarize older turns into a compact embedding and append it to the prompt as a single provenance-backed memory rather than passing all raw text.
Retrieval-augmented pipelines should be architected as a multi-step process: chunk and index content with rich metadata, run vector search, perform lightweight lexical reranking, then assemble a grounded context for the generator. How do you prevent hallucinations? Always attach provenance and confidence metadata to retrieved passages and surface them in the response when factuality matters. Use hybrid ranking (embedding similarity + BM25) for noisy document collections, and implement a reranker model when precision matters—this is especially relevant for support and compliance scenarios where you must cite the source.
The dialogue policy layer enforces business rules, safety constraints, and escalation logic; choose a hybrid strategy that mixes deterministic rules for compliance-sensitive paths with learned policies for conversational flow. For example, implement a simple threshold rule: if intent_confidence < 0.6 or safety_flag == true then route to human; otherwise proceed to automated action. Log every policy decision with inputs and outputs so you can replay edge cases and train a supervised policy model from real interactions. Human-in-the-loop workflows should be fast and contextual: surface the retrieved evidence, conversation summary, and suggested response to agents to minimize cognitive load.
Finally, treat deployment and observability as first-class architecture concerns: containerize model services, autoscale based on request queues and GPU utilization, and enforce strict latency SLOs with prioritized queues for real-time voice interactions. Instrument traces that cross NLU, vector search, and LLM calls and capture end-to-end metrics like task completion and escalation frequency for continuous improvement. Version your models and prompt templates, run canary experiments for policy changes, and automate retraining pipelines using production conversation logs to prevent drift. Building this plumbing lets us move from prototypes to reliable conversational AI systems that meet both user expectations and operational constraints.
Fundamental Technologies and Models
When you pick technologies for a production conversational AI stack, the choices you make at the model and infra layer determine whether the assistant is accurate, fast, and maintainable. In practice we lean on two families of building blocks: dense neural models (the large language models we prompt or fine-tune) and retrieval systems built on vector search. Choosing how and when to use each shapes latency, factuality, and the ease of auditing responses.
Transformers remain the de facto architecture behind modern generative models; they convert tokenized text into contextual embeddings that capture semantics. Define embeddings as fixed-size numeric vectors representing meaning; these let you compare text with cosine or dot-product similarity. You should treat tokenization, position encoding, and attention patterns as first-class tuning knobs: they affect effective context length, truncation behavior, and how well the model preserves entity fidelity across long turns. When we talk about large language models, we mean transformer-based generative networks trained on broad corpora and often instruction-tuned to follow prompts.
Retrieval-augmented patterns use vector search to ground generation in trusted documents instead of relying on the model’s latent memory alone. Vector search here means indexing embeddings in an approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) index so you can return semantically similar chunks in milliseconds. In production you’ll chunk documents with overlap, attach provenance metadata, and run a hybrid reranking stage (embedding score + lexical BM25) before passing top passages to the generator. This approach reduces hallucination risk while preserving fluent output.
For response generation you’ll balance model size, tuning method, and cost. Fine-tuning a base model or applying lightweight adapter techniques such as LoRA (low-rank adaptation) gives you domain alignment without retraining billions of parameters. Instruction tuning aligns model behavior to prompts and safety policies, while distillation/quantization helps meet latency and memory constraints on CPU or small-GPU hosts. We recommend evaluating models for factuality, response diversity, and calibration, not just raw perplexity.
Combine retrieval and generation through a clear orchestration pattern so the runtime is predictable and auditable. For example, run NLU to classify intent, trigger vector search when intent requires external knowledge, rerank results, and then call the generator with a provenance-backed prompt. A minimal orchestrator looks like this:
intent = classify(text)
if intent.requires_knowledge:
docs = vector_search(query, k=10)
candidates = rerank(docs, query)
prompt = build_prompt(text, candidates[:3])
response = generate(prompt)
else:
response = template_render(intent, slots)
This pattern keeps grounding explicit and enables logging every decision that prefaced a generated reply.
Operational constraints push engineering choices: quantize models for lower memory, batch inference to maximize GPU throughput, and cache recent embeddings or assembled prompts to reduce repeated vector queries. Manage context windows with sliding-window summaries stored in your vector DB so we preserve long-term memory without exploding prompt size. For voice or low-latency use cases you may choose smaller on-device models for immediate responses and defer heavy grounding to backend services.
Safety and observability must be built into the model layer. How do you detect when the model is hallucinating or drifting? Use a combination of automated fact-check classifiers, provenance-checks that require citations for factual claims, and policy gates that route low-confidence responses to deterministic templates or human agents. Instrument intent confidence, reranker precision, generation confidence proxies, and downstream business metrics (task completion, escalation rate) so you can close the loop with retraining or prompt changes.
Taking these technology choices together, we can then reason about orchestration patterns, caching strategies, and evaluation pipelines that scale — the next step is integrating vector search with prompt templates, choosing where to cache context, and designing retraining workflows that prevent regression and keep the assistant aligned with business goals.
How Conversational AI Works
Building on this foundation, the runtime behavior of a production conversational AI determines whether users get a reliable answer or a baffling hallucination. We design the orchestrator as the single decision point that enforces timeouts, routes calls, and composes context; this keeps orchestration auditable and lets us swap model components without changing routing logic. In practice you’ll see this manifested as a lightweight control plane that calls NLU, consults a fast cache, triggers vector search when needed, and finally decides between a deterministic template, a retrieval-augmented generator, or a human handoff. Treat the orchestrator as policy enforcement first and request coordinator second to keep failure modes explicit and testable.
State management shapes the conversation experience more than raw model quality. Store ephemeral session state (slots, turn history, policy flags) in a low-latency store like Redis for immediate lookups, and persist canonical summaries and embeddings in a vector DB for long-term recall. Use sliding-window summarization to compress older turns into a single provenance-backed memory so you don’t blow the token budget while preserving user-relevant facts. When you preserve both short-lived slots and long-term embeddings, you can support task-oriented flows that resume across sessions and open-ended assistance that remembers prior preferences.
Grounding is where retrieval-augmented approaches earn their keep: fetch semantically similar passages with vector search, then rerank and attach provenance before generating text. Instead of feeding raw search hits to the generator, build a provenance-aware prompt that cites documents and includes confidence scores; that makes downstream fact-checking and audits straightforward. You should chunk content with overlap, run a hybrid reranker (embedding score plus lexical match), and include only the top grounded passages in the prompt to reduce hallucination. This pattern lets a large language model provide fluent language while remaining tethered to verifiable source material.
Prompt engineering and prompt assembly are operational tasks, not creative hobbies. Construct prompts that separate user intent, system instructions, and retrieved evidence, and always include explicit instructions about how to use—or ignore—each piece of evidence. For example, assemble a prompt that prefixes each retrieved passage with a source id and confidence, then ask the model to answer and cite sources when making factual claims:
User: "Why was my refund denied?"
Evidence: [doc-42 | 0.92] "Refunds denied if order > 90 days"
Evidence: [policy-Refund | 0.88] "Non-refundable items: gift cards"
System: "Answer using evidence first; if no evidence matches, ask a clarification question."
How do you decide when to call an LLM versus a template? Use deterministic templates for compliance-sensitive responses and low-latency needs; call a retrieval-augmented large language model when you need natural phrasing, synthesis across documents, or empathetic tone. Implement confidence thresholds and safety gates: if intent_confidence < threshold or retrieved evidence is inconsistent, fall back to templated language or escalate to an agent. Batching, caching of recent prompts, and quantized model variants reduce cost and latency while preserving responsiveness for real-time voice or chat.
Operationalizing safety and observability turns guesses into continuous improvement. Log every decision: intent scores, reranker ranks, prompt text, model outputs, and policy outcomes so you can replay edge cases and train supervised policy models. Instrument E2E metrics—task completion, escalation rate, latency—and correlate them with model-level signals like generation confidence proxies and reranker precision. Use regular human-in-the-loop reviews and A/B tests to validate prompt changes, policy tweaks, and retraining cycles so drift is detected before it harms users.
Taken together, these engineering choices determine whether a conversational AI scales from prototype to production-grade assistant. Tune orchestration rules, summarize memory prudently, ground generations with vector search, and enforce explicit policy gates so responses remain accurate and auditable at scale. Next, we’ll translate these runtime patterns into concrete model-selection and deployment strategies that balance latency, cost, and factuality for your specific use cases.
Design and Implementation Best Practices
Building on this foundation, start by treating reliability, factuality, and safety as design constraints rather than optional features; conversational AI that delights in demo fails quietly in production. The first design decision is explicit: decide where determinism must win (compliance, billing, refunds) and where generative flexibility is acceptable (helpful suggestions, tone). When we make those trade-offs up front, we can select patterns—retrieval-augmented grounding, deterministic templates, or hybrid policy—that map directly to business risk and user experience goals. Front-loading these constraints reduces scope creep later and keeps implementation decisions traceable.
Separate control and data planes and enforce an orchestrator-as-policy model to keep runtime behavior auditable and testable. How do you ensure low-hallucination, low-latency responses at scale? Route requests through a single orchestrator that first runs fast NLU, then conditionally triggers vector search, reranking, and an LLM only when necessary; if any step exceeds its latency budget, the orchestrator falls back to a template or cached summary. This pattern lets us enforce circuit breakers, timeouts, and routing rules centrally so changes to models or indices don’t silently alter user-facing behavior.
Manage state across two complementary stores: a low-latency session cache for ephemeral slots and turn history, and a canonical vector-backed memory for long-term facts and summaries. Store short-lived conversation variables in Redis-like stores for instant policy checks and slot-filling; persist summarized embeddings and provenance into your vector database so the assistant can recall previous orders, preferences, or conversation summaries across sessions. Use sliding-window summarization to compress old turns into a single vector-plus-summary; this preserves salient facts without blowing token budgets and lets you rehydrate long-term context when the dialog requires it.
Design retrieval as a multi-step pipeline that prioritizes precision and provenance. Chunk documents with overlap, index embeddings in an ANN (approximate nearest neighbor) store for fast vector search, then apply a hybrid reranker that combines embedding similarity with lexical signals (for example, BM25) and optionally a learned cross-encoder for high-precision results. Always attach source ids, confidence scores, and timestamps to retrieved passages and include only top-ranked evidence in prompts so the LLM synthesizes from an auditable evidence set. This retrieval-augmented approach limits hallucination while preserving the fluency advantages of generative models.
Embed policy and safety checks at multiple layers so business rules are enforced even when model behavior drifts. Implement deterministic templates for compliance-sensitive replies and enforce simple threshold rules upstream—for instance, if intent_confidence < 0.6 or evidence_conflict == true, route to human or templated fallback—then log the entire decision context for replay. Surface suggested responses, evidence, and conversation summaries to human agents in assisted-handling workflows to reduce cognitive load and speed interventions. Version policy rules and prompt templates alongside models so you can roll back behavioral changes through standard CI/CD practices.
Operationalize observability, deployment hygiene, and cost controls as part of implementation rather than afterthoughts. Instrument traces across NLU, vector search, reranker, and LLM calls, set SLOs for end-to-end latency, and prioritize traffic into real-time and background queues; use canary deployments and A/B experiments when changing prompts or policies. Reduce inference cost with quantization, batching, and cached prompts for repeated queries, and autoscale model services based on GPU utilization and request queue depth. By designing for auditability, graceful degradation, and operational metrics from day one, we make it possible to evolve models and orchestration patterns safely as requirements change and prepare to choose specific model and deployment strategies next.
Business Use Cases and Examples
Building on this foundation, conversational AI delivers measurable business impact when you map capabilities to concrete workflows like support, sales, and internal knowledge work. In customer support, for example, retrieval-augmented flows grounded by vector search let you answer factual queries—order status, refund policy, SLA windows—with provenance attached so responses are auditable. When accuracy matters, you should prefer retrieval-augmented grounding over free-form generation; this reduces hallucinations and simplifies compliance. How do you decide which pattern to use for a given channel? Use intent confidence, required factuality, and latency budget as your primary decision signals.
Start with the high-volume, low-risk scenarios where automation yields the fastest ROI. Route common support intents—password resets, order lookups, shipping windows—through deterministic templates or hybrid templates seeded by retrieved snippets so you get correctness and speed. For escalations that require synthesis across multiple documents, call a retrieval-augmented generator that presents candidate passages and a suggested reply for an agent to approve. This human-in-the-loop approach speeds resolution while preserving control: agents see source ids, confidence scores, and a one-click accept/modify UI that reduces cognitive load and errors.
Sales and marketing use conversational AI to accelerate lead qualification and content personalization. For instance, embed an assistant on a product page that asks qualifying questions, fills structured CRM fields, and then surfaces personalized assets using vector search over case studies and whitepapers. In outbound or nurture sequences, combine an NLU classifier to detect intent and urgency with a generation layer that tailors tone and key points—while using templates for regulatory phrases. This hybrid pattern increases conversion by keeping creative language flexible but anchoring claims to retrievable evidence.
Internal tooling and developer productivity are underused but high-value applications. Give engineering teams an on-demand runbook assistant that searches repo docs and incident retrospectives via vector search, returns ranked snippets, and synthesizes next steps. When you integrate with CI/CD and observability tools, the assistant can propose remediation commands or open PR templates—always showing the provenance that produced the suggestion. This reduces mean time to resolution and preserves audit trails for postmortems while keeping automation reversible.
Compliance-sensitive domains like banking, healthcare, and legal demand stricter guardrails. In these contexts, prefer deterministic templates for policy statements and use retrieval-augmented answers only when every factual claim must cite a source. Implement policy gates that block free-form responses when intent_confidence < 0.65 or evidence_conflict == true, and require human sign-off. We’ve seen teams triage these requirements by versioning templates and prompt policies in CI/CD so behavioral changes are testable and revertible—this keeps regulatory auditability compatible with iterative model improvements.
Finally, measure business outcomes, not just model metrics. Track end-to-end task completion, escalation frequency, revenue influenced, and average handle time alongside intent accuracy and reranker precision so you can correlate technical changes with business KPIs. Use A/B tests to compare purely templated flows against retrieval-augmented assistants and monitor customer satisfaction and operational cost. By mapping each use case to expected outcomes and instrumenting provenance, we can safely expand conversational AI across channels while maintaining control, traceability, and measurable ROI.