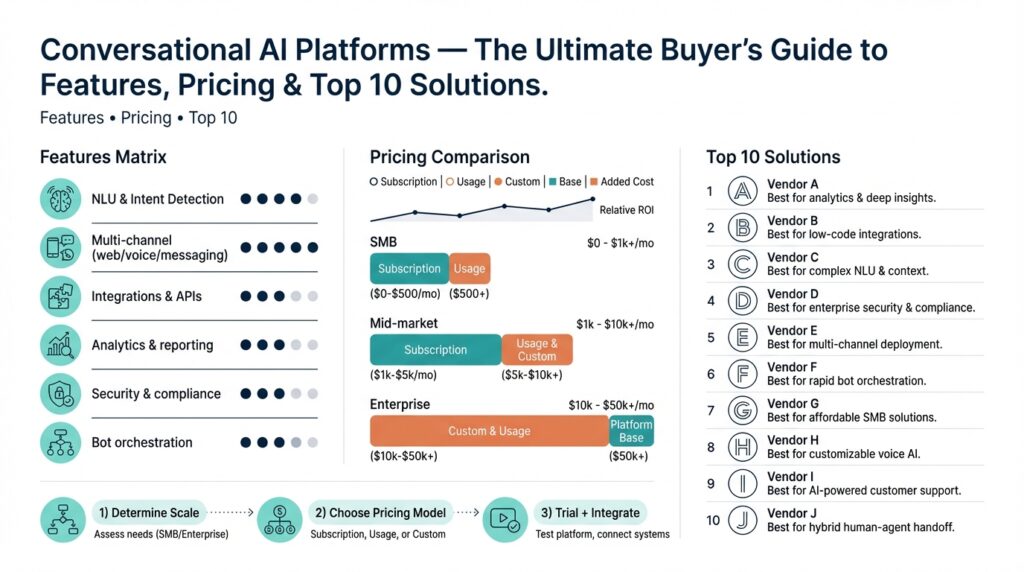
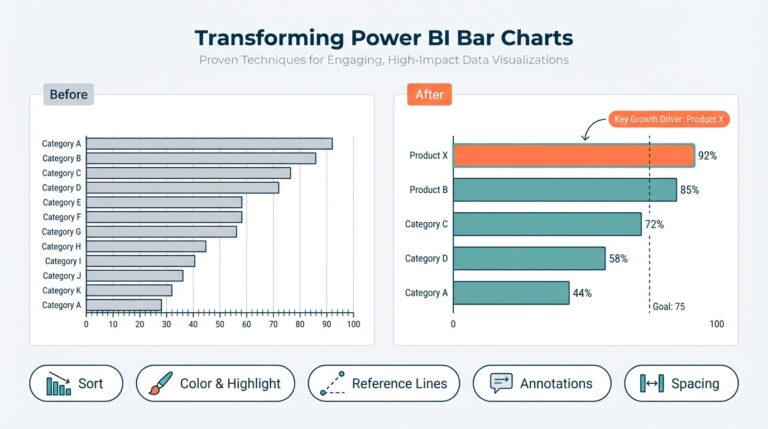
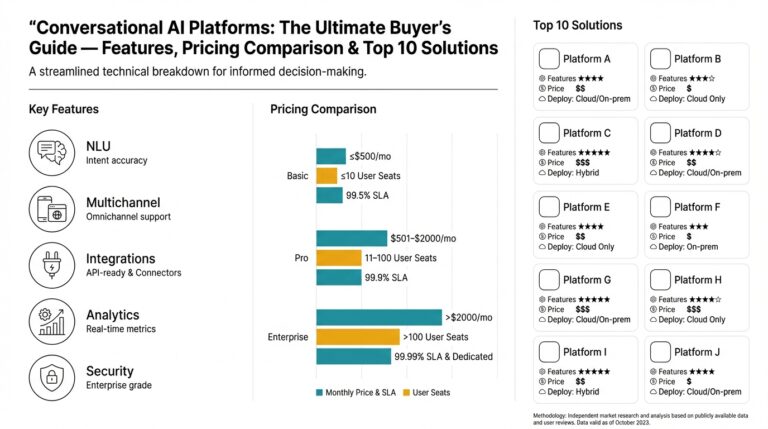
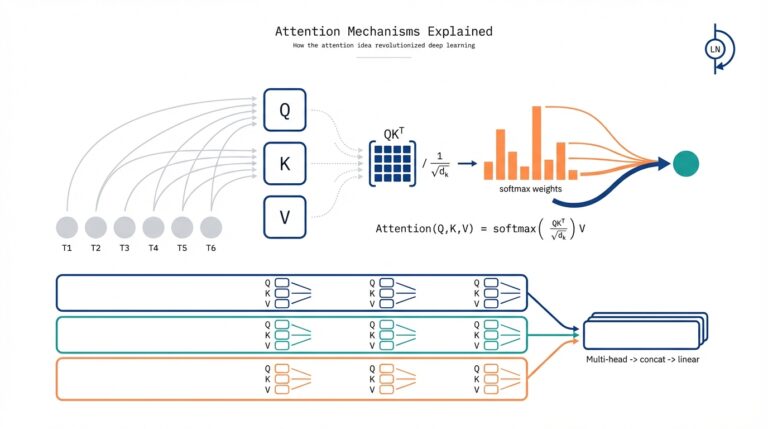
Why Conversational AI Matters
Conversational AI has moved from novelty to business-critical infrastructure because it changes how users interact with systems at scale. In the first interaction with a customer you want reliable intent recognition, contextual follow-up, and consistent tone—capabilities that modern conversational AI platforms provide through models, orchestration, and tooling. When you evaluate platforms, prioritize how they combine natural language understanding with robust engineering features, because that combination determines whether a solution will perform in production or fail under real-world load.
The most immediate reason you should care is impact on customer-facing metrics: response time, first-contact resolution, and containment rate. Deploying chatbots and virtual assistants reduces reliance on synchronous human labor by automating routine requests and triaging complex ones, which lowers operational cost and improves availability. Moreover, conversational AI enables new revenue pathways—guided purchases, proactive notifications, and in-app conversational commerce—because it converts passive interfaces into interactive, stateful experiences that can be instrumented and optimized.
From an engineering standpoint, the value shows up in integration velocity and observability. We treat the conversational layer as another microservice: it needs stateless endpoints for session handling, downstream call patterns for business logic, and telemetry hooks for intent and slot-level metrics. Therefore, platform choice affects your CI/CD pipelines, data pipelines, and monitoring stacks; if the platform lacks exportable event streams or extensible webhooks, you’ll spend time building brittle adapters. In contrast, platforms that provide native analytics, versioned models, and test harnesses allow you to iterate quickly while maintaining traceability and compliance.
User experience is where conversational AI earns trust or loses customers, so design for multi-turn context and graceful fallbacks. Effective systems maintain short-term and long-term context, surface clarifying questions when confidence is low, and escalate to human agents with conversation history intact. This human-in-the-loop pattern reduces failure modes and improves model training data because agents can label and correct interactions inline. Consequently, you avoid oscillating behavior where the assistant repeats errors or silently fails on ambiguous queries.
Consider a concrete scenario: an e-commerce app that uses a conversational layer for order tracking, returns, and product recommendations. When a user asks “Where’s my refund?” the system must map that intent, call the payments service, interpret status codes, and translate backend timestamps into user-friendly ETA—often across multiple APIs and authorization boundaries. Building that reliably requires support for transactional API calls, secure token management, and a session model that preserves user context across channels. In practice, teams that treat conversational AI as an integration challenge—not only an NLP problem—release features faster and reduce post-launch defects.
How do you know a conversational AI investment is paying off? Measure end-to-end business KPIs tied to conversations: containment rate (percentage of queries resolved by the assistant), average handle time for escalations, conversion uplift for guided flows, and annotation-driven intent accuracy. Track model-driven metrics alongside platform observability: utterance confidence distributions, fallback frequency, and conversation dropout points. Use A/B testing to validate conversational UX changes and monitor long-run drift so you can schedule model retraining and data retention policies proactively.
Building on this foundation, the practical next step is evaluating platform trade-offs—feature completeness versus engineering flexibility, pricing versus throughput guarantees, and hosted model constraints versus self-hosting needs. As we move into feature and pricing comparisons, keep these technical priorities top of mind: observable event streams, context management, robust fallback handling, and privacy controls that match your compliance requirements. That focus will help you separate marketing claims from platforms you can operate reliably in production.
Core Features to Compare
Building on this foundation, the first thing to evaluate is how the platform implements core NLP capabilities: intent recognition, entity/slot extraction, and confidence scoring. How do you measure model performance in your pipeline—precision, recall, and utterance-level confidence distributions—or do you rely on opaque vendor metrics? You want a platform that gives exportable evaluation artifacts (confusion matrices, per-intent F1) and supports model customization or transfer learning so you can move from generic intent recognition to industry-specific models without retraining from scratch.
Beyond raw NLU, compare context management and session models because state handling determines UX quality across retries and escalations. Assess whether the platform offers short-lived session state, long-term memory for user preferences, and deterministic slot-filling semantics; also check TTLs and mechanisms for context eviction. For example, preserving order IDs and authorization tokens across channels matters when you escalate a chat to a human agent—look for token refresh hooks and secure session stores rather than platforms that dump context into ephemeral cookies.
Integration and orchestration capabilities are the next practical differentiator you’ll notice in production. Verify native SDKs, webhook patterns, and prebuilt connectors for CRMs, payment gateways, and identity providers; these reduce glue code and speed integration velocity. Also evaluate orchestration features: can you execute parallel API calls, coordinate compensating transactions, and set idempotency keys like X-Idempotency-Key on retries? Platforms that let you compose microservice calls inside a flow reduce latency and error surface compared to ones that force every integration into external middleware.
Observability, testing, and versioning are non-negotiable for operating at scale. Demand event streams (Kafka, Kinesis, or webhooks) with schema-stable payloads that include intent, slots, and confidence so you can build downstream analytics and drift detectors. Check for built-in test harnesses that replay historical conversations, A/B testing support for conversational variants, and model/version tagging so rollbacks are safe. Track business KPIs alongside model telemetry—containment rate, fallback frequency, and average time-to-escalation—to tie conversational improvements to revenue or cost savings.
Fallback handling and human-in-the-loop workflows determine your system’s resilience when NLU fails. Compare how platforms surface low-confidence interactions: do they prompt clarifying questions, route to skill-based queues, or create review tasks for annotators? Effective platforms provide annotation UIs where agents correct intents inline and feed that data back into retraining pipelines; this closes the loop between production failures and model improvements. Also evaluate SLA-backed routing, context-preserving escalations, and throttling controls that protect downstream systems under bursty load.
Security, compliance, and deployment options often make the procurement decision rather than feature checkboxes. Verify data residency, encryption-at-rest and in-transit, and RBAC/audit logs; for regulated domains you’ll need exportable audit trails and configurable data retention policies. Consider hosting models: when should you choose a managed hosted model versus self-hosting for latency and privacy? Finally, compare throughput guarantees, per-minute rate limits, and pricing models against expected conversational throughput—these operational constraints shape architecture and integration choices more than marketing claims. With these technical comparisons in hand, we can pivot to pricing and trade-offs next to map features to real-world cost and operational burden.
Pricing Models and Cost Drivers
Cost surprises are the number-one procurement risk for conversational AI: you can sign a deal thinking you bought a chatbot and discover months later that high-throughput flows, long context windows, or frequent fine-tuning doubled your bill. Building on this foundation, we need to treat conversational AI pricing as a capacity planning problem rather than a per-seat SaaS checkbox. You and your finance team should expect variable usage patterns—peak promotional windows, multi-channel spikes, and human escalation—that interact directly with pricing models and drive spend unpredictably.
There are several common pricing models you’ll encounter, and each shapes architecture decisions. Subscription and tiered plans trade variable cost for predictability, pay-as-you-go charges per request or per token and scales with usage, while throughput- or concurrency-based pricing charges for reserved capacity and guaranteed latency. Enterprise agreements add committed spend discounts, feature-based add-ons (analytics, connectors), and professional services fees; self-hosting flips the equation to capital and operational expenditures for infrastructure, operational staffing, and model licensing.
Understanding the primary cost drivers lets you forecast and optimize. Throughput—requests per minute—and average message size (tokens or characters) are the dominant inputs for token-based or per-request models, while model complexity (small intent models versus large generative models) changes per-call compute cost dramatically. Other drivers include context window length (more tokens retained means higher inference cost), concurrency guarantees (reserved CPU/GPU), data retention and logging requirements, and the frequency of fine-tuning or retraining cycles.
Translate those drivers into a simple cost-per-resolution calculation to make trade-offs explicit. For example, compute platform cost + storage and logging + annotation/human fallback + integration/connector fees, divided by resolved conversations, yields the effective cost per containment. If platform + infra = $6,000/month, human fallback = $9,000/month, and you resolve 50,000 conversations, cost per resolution = ($6,000 + $9,000)/50,000 = $0.30. Run this arithmetic with your expected containment rate and conversions to compare feature choices (larger model that raises containment by 2% vs cheaper model plus more escalations).
Beware of hidden and recurring add-ons that inflate total cost beyond headline rates. Fine-tuning, custom model hosting, private data residency, compliance audits, long-term analytics storage, and premium connectors for CRMs or telephony often appear as separate line items; annotation tools and human-in-the-loop review systems produce continuous operational costs that scale with conversation volume. Also factor migration costs and the operational overhead of versioning, schema changes in event streams, and retention policies required by your auditors.
How do you forecast spend for a conversational AI deployment? Start by load-testing realistic user journeys to measure tokens-per-session and service-level needs, then simulate peak scenarios. Use hybrid strategies to optimize cost: route high-value, short-session intents to smaller deterministic models, reserve large LLM calls for complex generative tasks, cache frequent responses, and batch asynchronous jobs. Instrument metrics that map directly to spend—tokens per session, requests per minute, containment rate, and cost per resolution—and add budget alerts and hard throttles in the procurement contract.
When negotiating, use contractual levers to align platform incentives with your operational goals. Ask for committed throughput discounts, predictable overage pricing, explicit SLAs for latency and rate limits, and the option to bring-your-own-model or export training artifacts. Taking this approach ties pricing models and cost drivers back to measurable business KPIs so you can choose features that deliver ROI and avoid surprises as you scale.
Deployment, Security, Compliance
When you push a conversational AI project into production, the biggest failure modes aren’t model accuracy but deployment choices and governance gaps. Building on this foundation, you must align hosting topology, data residency, and access controls with both latency targets and regulatory obligations—before you write integration glue. How do you design an architecture that satisfies low-latency customer journeys while meeting corporate security policies and external compliance audits? Framing those trade-offs early prevents expensive rework when auditors or SREs demand isolation or exportable logs.
Choose the right hosting model based on risk and operational capability: managed cloud, VPC-backed SaaS, private cloud, or full self-hosting. Each option shifts responsibility: managed vendors take operational burden but may limit data residency and model control; self-hosting gives you model sovereignty and private networking at the cost of staffing and patching. For latency-sensitive flows we route intent classification to local, smaller models and reserve large generative calls for an isolated inference cluster; this hybrid deployment reduces cost, preserves privacy, and simplifies rollout during peak traffic.
Security must be architected into the pipeline rather than bolted on at the API layer. Enforce encryption-in-transit (TLS 1.2+) and encryption-at-rest with a centralized KMS that supports key rotation and auditability; integrate platform RBAC with SSO and least-privilege service accounts so production secrets never live in app code. Implement short-lived access tokens and scoped refresh hooks for downstream APIs; for idempotent operations add an idempotency header to protect against retries, for example:
POST /v1/converse
Authorization: Bearer <short-lived-token>
Idempotency-Key: 9f1b2a3c-4d5e
Content-Type: application/json
These patterns reduce blast radius and make security reviews practical.
Data governance is the control plane for auditability and compliance. Define clear data residency and retention policies that map to your regulators’ expectations, and apply pseudonymization or deterministic hashing for PII before it enters model training or analytics streams. When should you retain raw conversation logs versus sanitized telemetry? Retain raw logs only under controlled, auditable conditions with exportable audit trails and automated retention deletion; expose only aggregated metrics for analytics. Maintain an evidence trail that ties a decision to the exact model version, input utterance, and configuration used at the time.
Operational controls close the loop between security and continuous improvement. Emit immutable, schema-stable event streams (Kafka, Kinesis) containing intent, confidence, and slot-level metadata so you can replay conversations in test harnesses and prove lineage during audits. Instrument fallback and escalation events with correlation IDs to reconstruct timelines for incident response and compliance verification. Schedule regular penetration tests and tabletop exercises that exercise escalation flows, data exfiltration scenarios, and human-in-the-loop annotation systems to validate that RBAC, throttles, and audit logs behave as expected.
In practice, an e-commerce order-tracking assistant shows these trade-offs plainly: we host intent routing in a VPC-backed microservice to reduce latency and keep order IDs within the customer’s region, while generative summarization runs in an isolated cluster with strict export controls. Escalations carry an ephemeral token and a conversation snapshot stripped of PII; agents receive context via a secure session store, not raw logs. Negotiate SLAs that include throughput, retention guarantees, and the right to export training artifacts so you can onboard a new vendor or perform independent audits without data loss.
Treat these operational, security, and compliance decisions as procurement-level requirements rather than post-deployment checkboxes. Building on this foundation, you’ll be able to compare platforms not just on model quality but on whether their deployment and governance primitives align with your legal, security, and operational constraints—the next step is mapping those choices to pricing and operational overhead so we can quantify cost versus control.
Integration and Extensibility Options
Integration and extensibility are the glue that turns a conversational AI proof-of-concept into a production service you can operate and evolve. When you evaluate platforms, watch for first-class API support, webhook patterns, SDKs for your stack, and exportable event streams in the first interaction—these determine how fast you can connect business systems and how safely you can extend behavior. You want integration to be predictable and extensibility to be deliberate, because brittle adapters and opaque extension points are where outages and technical debt accumulate. In short, integration and extensibility shape your delivery velocity and long-term maintenance burden.
There are three practical integration patterns you’ll use repeatedly: SDKs and client libraries that embed conversational features into your application, webhook- or event-driven connectors that notify your services when state changes, and prebuilt connectors for common systems like CRMs, payment gateways, and identity providers. How do you choose between a webhook-first model and an SDK-centric approach? Use SDKs when you need tight latency and embedded session handling; prefer webhooks and event streams for decoupled processing, analytics, and long-running operations. Prebuilt connectors accelerate onboarding, but confirm they allow customization—connector code you can extend is far more valuable than a closed, one-off integration.
Compose integrations inside the conversational flow when possible rather than outsourcing orchestration to brittle middleware. That means your conversation runtime should support parallel API calls, timeout policies, retry strategies, and idempotency keys so retries don’t double-bill or create duplicate side effects. For example, set an idempotency header on outbound calls and correlate it with your conversation ID: Authorization: Bearer
Extensibility should feel like a plugin system: custom actions, skill SDKs, and sandboxed scripts that run alongside core NLU but are governed by versioning, RBAC, and dependency controls. When you implement custom actions for domain logic—inventory checks, payment captures, personalized recommendations—encapsulate them so you can swap implementations without touching training data or conversation flows. Moreover, require backward-compatible extension contracts and semantic versioning for any public action; that practice prevents sudden regressions in production when teams deploy new logic or upgrade libraries.
Developer experience and observability make integration sustainable. Provide a local emulator, CI-friendly test harness, and contract tests that validate webhook payloads and connector behavior before deployment. Emit schema-stable event streams containing intent, slots, confidence, and correlation IDs so you can replay conversations, run drift detection, and reconstruct incidents. Don’t forget operational integration concerns: short-lived tokens, automatic refresh hooks for downstream APIs, and centralized secrets management are essential to keeping integrations secure and auditable as volume grows.
Finally, align integration and extensibility choices with operational and commercial constraints: map connector maturity to expected maintenance costs, measure how much logic lives in the platform versus your services, and negotiate vendor rights to export connectors, training artifacts, and event histories. Taking a hybrid approach—local SDKs for latency-sensitive routing, event streams for analytics, and isolated clusters for heavy inference—usually balances cost, control, and developer velocity. Building on this foundation, the next step is to translate these integration trade-offs into pricing and governance decisions so you can choose a platform that fits both your technical architecture and procurement constraints.
Evaluation Checklist and PoC
Building on this foundation, start your evaluation by treating the pilot as a tightly scoped engineering experiment rather than a marketing demo. Conversational AI projects fail when teams conflate feature tours with integration readiness, so define measurable acceptance criteria up front: functional correctness for core intents, measurable containment uplift, latency within SLOs, and secure, auditable data flows. Make those criteria visible to stakeholders and tie them to business KPIs—containment rate, average handle time, and cost per resolution—so the proof-of-concept maps directly to operational outcomes.
Define the technical gates that will decide whether you move from prototype to production. How do you know when a proof-of-concept earns production rollout? Require reproducible evaluation artifacts: per-intent precision/recall or F1, utterance-level confidence distributions, confusion matrices you can export, and a replayable transcript set that runs in your test harness. Building on the earlier discussion about observability and versioning, insist that the platform emits schema-stable event streams (intent, slots, confidence, correlation IDs) during the pilot so you can validate analytics, detect drift, and prove lineage for audits.
Scope the integration footprint for the pilot to minimize variables while exercising core constraints. Start with the smallest user journey that touches authentication, one or two downstream APIs, and a fallback path to agents; for example, an order-status flow that validates tokens, calls payments and shipping services, and returns a human-escalation snapshot. Instrument idempotency headers, short-lived tokens, and correlation IDs in those calls so retries are deterministic and post-mortem reconstruction is possible. This focused scope reduces noise in performance testing and isolates where errors originate.
Set explicit performance and resilience targets and validate them under realistic load. Specify throughput and latency SLOs (for example, p95 response under X ms and sustainable RPS over Y minutes) and run load tests that mimic promotional spikes and concurrent escalations. Verify graceful degradation patterns: cache-first routing for high-frequency queries, fallback prompts when confidence < threshold, and capacity throttles that protect downstream services. Capture failure-mode telemetry—fallback frequency, escalation latency, and token refresh errors—and make those metrics part of your exit criteria.
Operational readiness must be assessed in parallel with model performance. Require the pilot to demonstrate CI/CD for conversation flows, versioned models with safe rollback, and a test harness that replays historical conversations into each build. Validate human-in-the-loop workflows by having agents correct intents inline and measuring annotation throughput and label quality. Confirm compliance controls: configurable retention policies, PII masking before analytics, RBAC-integrated access, and exportable audit trails so you can prove what data and model version produced a decision.
Conclude the pilot with a compact decision report that links technical findings to procurement levers and next steps. Include quantified KPIs (containment delta, cost per resolution, error-class breakdown), a migration risk checklist (connectors, data residency, SLA gaps), and a recommended rollout pattern—phased channel expansion, hybrid local inference for latency-sensitive intents, or reserved throughput for peak windows. Taking this approach gives you a defensible, engineering-first proof-of-concept that translates conversational AI promises into operationally verifiable outcomes and prepares the organization for full-scale deployment.