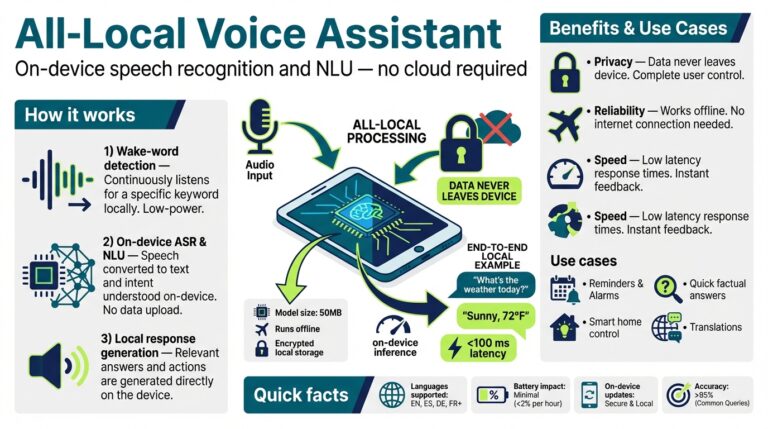
Understanding How Voice Assistants Work
Voice assistants have seamlessly integrated into our daily routines, from setting reminders to controlling smart home devices. But how do these virtual assistants actually work behind the scenes? At their core, voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Apple Siri, and Google Assistant rely on a combination of advanced technologies — including automatic speech recognition (ASR), natural language processing (NLP), and cloud computing.
First, when you speak to a device, your voice is captured and converted from analog sound waves into digital data. This process, known as ASR, allows the system to transcribe your spoken words into text. Major advancements in machine learning and deep neural networks have significantly boosted the accuracy of these systems in recent years. For more on this technology, you can explore IBM’s research on deep learning for speech recognition.
Once your request is transcribed, the assistant’s NLP engine attempts to understand the intent behind your words. For instance, saying “What’s the weather like tomorrow?” involves not just recognizing each word, but determining that you seek a weather forecast for a specific day. These models rely on vast datasets and knowledge graphs, allowing them to interpret context and user intent with remarkable precision. Scientific American provides an in-depth look at how AI understands and translates human language.
After understanding your intent, the assistant often connects to cloud-based servers to process the request, retrieve relevant information, and deliver a response. This connection is why most assistants require internet access for complex queries. For example, asking a voice assistant to play a certain song might result in a cloud query to streaming services. In contrast, simple actions—such as setting a timer—can sometimes be handled locally on the device.
It’s important to note that your voice data, especially when processed through the cloud, may be stored and analyzed to improve the system’s accuracy over time. This practice raises important questions around privacy and data security, topics you can read about in detail on the Federal Trade Commission’s guide on voice assistant privacy.
Understanding these steps reveals the complexity of voice assistant technology and highlights why security and privacy remain pressing concerns. Each stage — from voice capture and recognition to language understanding and response generation — can introduce potential risks for misuse if not properly managed.
Data Privacy Concerns and Eavesdropping Risks
Voice assistants such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri have become commonplace in modern homes and workplaces, offering convenience and hands-free operation for everyday tasks. However, beneath their helpful façade lies a range of privacy implications and potential eavesdropping risks that many users may not fully grasp.
How Voice Assistants Handle Your Data
When you interact with a voice assistant, your words aren’t simply processed locally and forgotten. Most of these devices send your audio commands to cloud servers, where they are transcribed, analyzed, and stored. This data is often used to improve the device’s performance, but it can also be used to construct detailed profiles of your habits, preferences, and personal routines. According to The Verge, tech giants sometimes retain user interactions far longer than buyers might expect, and such retention opens data up to potential misuse or breaches.
Risks of Eavesdropping and Accidental Recordings
One of the biggest fears about voice assistants is their “always listening” mode. Although they are meant to respond only after hearing a specific wake word, research—like the NPR investigation—has shown these devices can accidentally activate and record conversations without user intent. For example, a report from BBC News exposed that human contractors sometimes listen to snippets of recordings, purportedly for quality control, but this raises questions about who has access to your private moments.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
In 2018, a high-profile incident saw an Amazon Echo inadvertently record a family’s private conversation and send it to a random contact. As covered by CNET, the mishap highlighted how vulnerabilities in voice assistant systems can lead to severe breaches of privacy.
Steps to Mitigate Privacy Risks
- Review Voice Data Settings: Most platforms provide an account dashboard where you can manage or erase your voice history. Regularly review these settings and delete unnecessary recordings.
- Mute Microphones When Not Needed: Physically turn off your device’s microphone during private conversations or sensitive work, if your model allows.
- Limit Third-Party Access: Only enable trusted third-party apps and integrations. Each extra app can be a doorway for additional data collection.
- Stay Informed About Policies: Familiarize yourself with the privacy policies of your devices. The Electronic Frontier Foundation offers excellent resources to help users stay informed about their rights and the security posture of various voice platforms.
Understanding the privacy implications of voice assistants is crucial in a rapidly digitizing world. While these devices add unmatched convenience, users must remain vigilant to ensure their conversations and habits are not being exploited for unintended purposes. Diligence, regular audits of device settings, and a willingness to probe manufacturers’ privacy commitments are all key steps toward keeping your private conversations safe.
Security Vulnerabilities: Hacking and Unauthorized Access
Voice assistants have become a staple in many households and workplaces, offering convenience through hands-free control and smart automation. However, beneath the surface, these devices harbor a range of security vulnerabilities that could expose users to hacking and unauthorized access. Understanding these vulnerabilities—and how to guard against them—is crucial for anyone using voice-enabled technology.
How Hackers Exploit Voice Assistants
Voice assistants are constantly listening for their wake words, such as “Hey Siri” or “Alexa.” This always-listening mode can be a double-edged sword. Cybercriminals have demonstrated ways to exploit this feature by issuing commands using sounds inaudible to the human ear, known as ultrasonic attacks. In one notable example, researchers at Zhejiang University manipulated Alexa and Siri using frequencies outside the range of human hearing, gaining unauthorized control over the device and any connected smart devices in the home.
Additionally, attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in a device’s software or in the networks they are connected to. For instance, unencrypted data transmissions can be intercepted and manipulated, a practice known as man-in-the-middle attacks. In some cases, poorly secured APIs or outdated firmware leave devices wide open to being compromised remotely.
Case Studies and Real-World Incidents
The risk is not just theoretical. Multiple incidents have demonstrated that voice assistants can inadvertently expose sensitive information or be manipulated. In 2018, a family in Oregon discovered their Amazon Echo had recorded a private conversation and sent it to a contact without their knowledge. More alarmingly, researchers have shown that even TVs or radios can be used to “trick” assistants into executing commands if these commands are broadcasted in the environment. Such scenarios highlight the risk of attackers using disguised or hidden commands to trigger malicious actions.
Mitigation Steps and Best Practices
- Use Strong Authentication: Always enable authentication options provided by the device, such as voice recognition profiles or pin codes for sensitive commands.
- Update Regularly: Keep all devices—and their companion apps—updated to the latest firmware to protect against known exploits and vulnerabilities.
- Review Privacy Settings: Regularly audit what information is stored and shared through your assistant. Limit permissions to sensitive data and disable features you don’t need, such as “Drop In” on Amazon devices.
- Secure Your Network: Use strong, unique Wi-Fi passwords and enable WPA3 encryption on your router to prevent unauthorized network access, which could jeopardize all connected devices.
- Physical Placement: Avoid placing voice assistants near windows or exterior walls, where intentional or unintentional outside commands could be picked up.
For a comprehensive review of the security challenges posed by voice assistants, explore reports from institutions such as EFF and CSO Online. As voice-powered devices grow in popularity and sophistication, awareness and proactive security steps are vital in protecting your privacy and digital life.
The Threat to Personal and Household Security
Voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri have woven themselves into the fabric of our daily lives, controlling our smart home devices, setting reminders, and even handling online purchases. However, their growing presence in homes introduces significant risks that many users overlook, particularly when it comes to personal and household security.
One fundamental concern is the risk of unauthorized access. Voice assistants operate on far-field microphones, always listening for their wake words—”Hey Siri,” “Alexa,” and so forth. These devices can misinterpret similar-sounding words or even respond to voices on TV or radio, allowing unintended or malicious commands from more than just the homeowner. In recent years, researchers have demonstrated successful hacks where an attacker issues commands using sounds outside the range of human hearing, which are still picked up and executed by the assistant (see IBM Security Intelligence).
Another issue relates to privacy breaches. All conversations and commands around these devices are potentially susceptible to being recorded and stored, raising the risk of personal data leaks. In the event of a security breach, attackers could access voice logs containing sensitive details about your schedule, shopping habits, and even financial information. Major incidents, such as the accidental sending of private recordings to strangers, underscore how these devices can inadvertently expose household information (source: NBC News).
The threat isn’t limited just to eavesdropping; voice assistants are increasingly interconnected with other smart devices such as front door locks, security cameras, and thermostats. If a cybercriminal gains control over your assistant, they can unlock doors, disable alarms, or manipulate camera feeds without physical access to your home. A well-documented example involves hackers exploiting weak security settings or poorly chosen passwords to remotely control smart home devices through voice assistants (Consumer Reports).
Protecting your voice assistant and, by extension, your household, requires vigilance. It is crucial to set strong, unique passwords for your associated accounts, enable two-factor authentication, regularly review privacy settings, and mute the microphone when not in use. Staying informed with guides and tools from reputable sources like Cyber Aware can help users anticipate and minimize these risks.
Ultimately, while the convenience of voice assistants is undeniable, it is essential to recognize these hidden dangers and proactively manage their presence in our homes. Failing to do so leaves the door open to threats that could compromise not only privacy, but also the security of everyone under your roof.
Impacts on Children and Family Dynamics
As voice assistants such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri become central household tools, families are discovering new conveniences—and unexpected consequences. While these AI-driven helpers can streamline everything from shopping lists to bedtime routines, their influence on children and family dynamics is more intricate and subtle than many realize.
Early Technology Exposure and Social Development
When children interact with voice assistants, they learn that their commands are instantly executed, often with little need for ‘please’ or ‘thank you.’ This can impact how children perceive human interaction. Unlike parents or teachers who encourage politeness and patience, devices are programmed for immediate, transactional responses. Experts argue this might influence children’s communication habits, diminishing empathy and polite social behaviors. A study highlighted by NPR explores how smart speakers may alter the way children relate to adults, potentially eroding essential manners over time.
Privacy and Data Collection Concerns
Voice assistants continuously listen for wake words, raising privacy concerns, especially for families with young kids. Children are less equipped to understand privacy risks, and their voices and interactions may be recorded and stored by tech companies. According to research by the UK Children’s Commissioner, this data can create digital footprints that are difficult to erase and could potentially be misused in the future. Parents need to regularly review privacy settings, use parental controls, and educate children about digital safety to mitigate these concerns.
Changing Family Communication Patterns
Voice assistants can alter natural family interactions, sometimes creating silent household members who simply issue commands to technology instead of engaging with each other. For instance, asking Alexa to play music or answer a question can bypass discussion and joint decision-making. This may seem trivial, but over time, families might find themselves talking less, leading to potential feelings of isolation or weakening interpersonal bonds. A recent New York Times article describes families noticing a subtle but real shift in their communication as voice assistants become more commonplace.
Parental Controls and Setting Boundaries
To address these challenges, parents should consider implementing boundaries and using robust parental controls. For example, setting timers for device usage, restricting certain functionalities, and actively monitoring interaction history can help retain healthy technology habits. Experts at Common Sense Media recommend regularly discussing technology use and privacy as part of daily family conversation, helping children become more mindful users.
Modeling Healthy Behavior and Digital Literacy
The rise of voice assistants presents an opportunity for parents to teach digital literacy and responsible technology use. This involves not only setting rules but actively modeling respectful interaction with technology—such as saying ‘please’ and ‘thank you’ to voice assistants to reinforce good manners. Encouraging children to ask humans questions and seek in-person help before turning to an AI also helps maintain critical social skills and problem-solving abilities. Resources from Childnet International offer useful guidelines for navigating these discussions.
In sum, while voice assistants can offer families unprecedented convenience, it is vital to recognize and address their subtle impacts on children’s development and family relationships. Awareness, ongoing discussion, and active parental involvement are key to ensuring these tools support, rather than hinder, healthy family life.
Manipulation Through Targeted Advertising
As voice assistants become more integrated into our daily lives, their ability to collect and process personal information presents unique opportunities for targeted advertising. Unlike traditional forms of digital advertising, voice assistants can gather intimate details about users — such as daily routines, spoken preferences, and even emotional states — in real time. This access is not limited to words alone but can include tone, urgency, and contextual cues from conversations. With such a rich dataset, advertisers can craft highly personalized and sometimes manipulative ad experiences that users may not even realize are targeted specifically at them.
How Targeted Advertising Occurs via Voice Assistants
- Passive Data Collection: Voice assistants constantly listen for wake words, but during this process, they can inadvertently capture snippets of conversations. These recordings may be reviewed or analyzed by algorithms to detect interests or needs. For instance, discussing a vacation destination out loud may result in travel ads appearing soon after.
- Profile Building: Over time, every request — from asking for a new recipe to searching for nearby gyms — helps construct a digital profile. This profile can be used by advertisers to deliver offers that are precisely aligned with your habits and preferences, sometimes nudging you towards purchases without your conscious awareness. Learn more about this from studies published by the FTC.
- Personalized Interactions: Voice assistants can phrase advertising content as helpful suggestions, making it difficult for users to distinguish between unbiased recommendations and paid promotions. For example, an assistant might say, “Would you like to reorder your favorite shampoo from XYZ brand?” after noticing that it’s been several weeks since your last purchase, subtly guiding your consumer choices.
Real-World Examples and Consequences
Several reports have highlighted how interactions with voice assistants have directly influenced advertising strategies. In one case, a family noticed toys discussed near their device began appearing in online and in-app ads within days. Such examples underscore how voice data can be monetized, often without explicit consumer awareness.
This subtlety can be especially dangerous, as traditional advertising allows users to recognize and consciously consider marketing messages. However, with voice assistants, advertising can become woven into casual conversation, bypassing these critical filters. According to a report by Consumer Reports, the blending of recommendations and sales pitches can erode consumer trust and lead to unwanted purchases, data exposure, or even exploitation of vulnerable populations, such as children and the elderly.
Protecting Yourself from Manipulative Targeted Advertising
- Review Privacy Settings: Regularly check your device’s privacy policies and adjust how your data is collected and shared. Many voice platforms provide privacy dashboards to manage data retention and ad personalizations. The Google Assistant Help Center offers step-by-step guides for managing audio recordings and ad preferences.
- Limit Data Access: Only enable necessary permissions for your voice assistant. For example, if a feature requires access to your shopping history or email contacts for convenience, consider whether granting this access is worth the potential trade-off in privacy.
- Use Wake Words Intentionally: Some users go so far as to disable constant listening features, relying on manual activation to limit passive data collection. This proactive step can minimize the chances of unintended data capture.
- Stay Informed: Advertising practices are evolving rapidly; following updates from organizations such as the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) can help you stay ahead of new privacy concerns and advocacy efforts.
Ultimately, while voice assistants can offer unparalleled convenience, users must remain vigilant about the potential for manipulation through targeted advertising. By understanding these tactics and proactively managing privacy controls, you can enjoy the benefits of smart home technology without compromising your autonomy as a consumer.