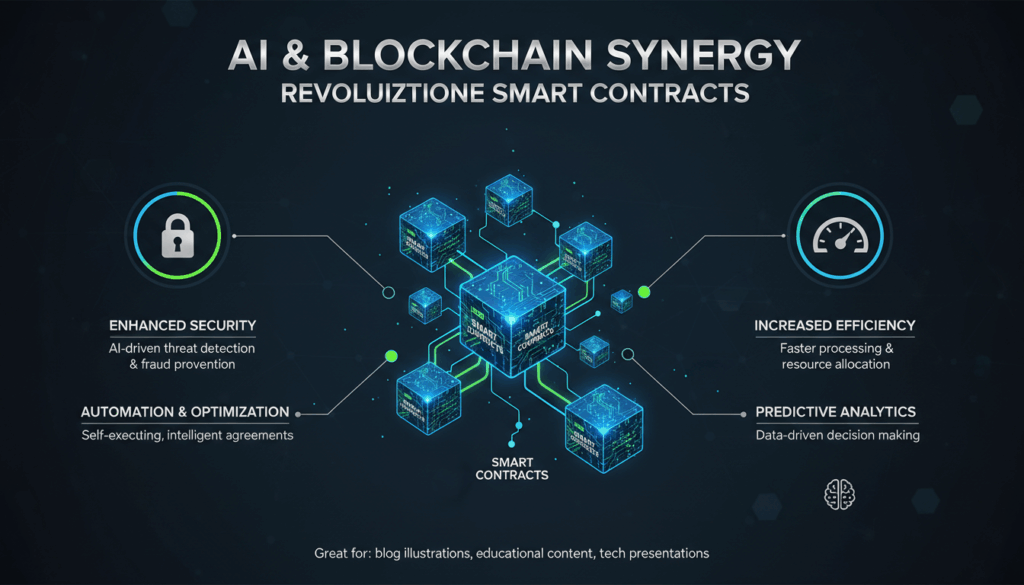
Introduction to Smart Contracts and Blockchain Technology
To understand the role of smart contracts within blockchain technology, it’s essential to delve into the mechanics and profound implications of these components. Initially conceptualized by Nick Szabo in the 1990s, a smart contract is essentially a self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. This technology thrives on blockchain platforms, such as Ethereum, where it finds practical application and widespread use.
Blockchain technology serves as the backbone for smart contracts. A blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that records transactions in a decentralized manner, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability. This decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries or third-party verification, which traditionally exerts control or influence over transaction validation.
Smart contracts execute automatically when predetermined conditions are met, similar to a regular contractual agreement. However, unlike traditional contracts, smart contracts do not depend on human intervention during execution, significantly reducing the risk of error and manipulation. For instance, consider a simple vending machine: when you select a product and insert the necessary amount of money, the machine automatically dispenses the item without requiring any additional supervision. Smart contracts operate under a similar mechanism but within a digital context.
These contracts are encoded on the blockchain, where they can initiate a variety of transactions and business logic autonomously. This feature opens a slew of possibilities across various domains:
-
Financial Services: Smart contracts streamline and automate processes such as insurance claims, mortgage agreements, and trade transactions. They ensure that all parties adhere to the terms without requiring a lengthy verification process.
-
Supply Chain Management: They enhance transparency and tracking, allowing stakeholders to verify the authenticity and movement of goods in real-time. For example, if a shipment arrives at a port, a smart contract can automatically release payment to the supplier.
-
Healthcare: By integrating secure data sharing, smart contracts can facilitate the exchange of patient information, treatment consents, and billing between healthcare providers and insurers, maintaining privacy and efficiency.
Ethereum is a popular choice for deploying smart contracts, given its Turing-complete programming language—Solidity—that allows developers to create complex contractual logic. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) provides a runtime environment that enables code execution, ensuring that smart contracts operate as intended across the network.
While the benefits are numerous, challenges do persist. Security vulnerabilities can exist, as with any software code, where bugs could be exploited for malicious purposes. Additionally, the immutability of the blockchain, while a strength, means that errors in smart contract code cannot be easily rectified once deployed.
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are beginning to augment smart contract capabilities. AI can enhance decision-making, anomaly detection, and adaptability, paving the way toward more intelligent, responsive smart contracts that can operate in complex, dynamic environments without the risks that human intervention might cause.
Together, smart contracts and blockchain technology represent a significant shift in how contracts and transactions are perceived and conducted, fostering a new paradigm of trust and efficiency in digital transactions.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Smart Contracts
Artificial Intelligence (AI) brings transformative capabilities to smart contracts, addressing several inherent challenges while unlocking potential applications. Through the infusion of AI, smart contracts can become more dynamic, adaptable, and intelligent. This symbiotic relationship between AI and blockchain technology can enhance the overall functionality and reliability of smart contracts.
AI’s primary contribution is its ability to enhance decision-making processes within smart contracts. Traditional smart contracts execute pre-defined conditions strictly as encoded, limiting their ability to adapt to unforeseen scenarios. AI, however, enables these contracts to process real-time data inputs, accommodating more nuanced decision trees based on predictive analytics. For instance, in a lending scenario, an AI-driven smart contract can dynamically adjust interest rates based on ongoing risk assessments and market conditions, making financial agreements more responsive and fair.
Furthermore, AI enhances the security of smart contracts. Machine learning algorithms can be employed to detect anomalies or unusual patterns in contract interactions, such as attempts at fraudulent transactions. By continuously learning from large datasets, AI systems can predict and identify potential vulnerabilities or breaches in real-time, proactively safeguarding the network.
AI also aids in automating contract management and compliance monitoring. In regulatory environments, AI-based smart contracts can ensure that all transactions adhere to legal requirements by automatically updating and verifying compliance data. For example, in supply chain contracts, AI can ascertain regulatory adherence and trace goods’ origins through intelligent data tracking and validation processes, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Additionally, AI can improve the scalability of smart contracts. As blockchain networks grow, maintaining efficiency becomes challenging. AI algorithms can optimize resource distribution and task scheduling, ensuring that the blockchain processes remain streamlined and responsive despite scaling pressures. This is crucial for industries like logistics and finance where transaction volumes can be significant.
Perhaps one of the most promising applications of AI-enhanced smart contracts lies in adaptive contracts, which are capable of learning and evolving from past interactions. These contracts, through machine learning, can continuously improve their decision-making criteria by analyzing historical data and outcomes, optimizing terms, and execution processes. For instance, insurance contracts could personalize coverage conditions based on a user’s behavior patterns, track risk variables, and adjust agreements correspondingly to promote fairer risk management.
The integration of AI into smart contracts represents a step toward more autonomous, efficient, and secure blockchain environments. By leveraging the analytical prowess of AI, smart contracts can transcend their static nature and become integral components of a more sophisticated digital infrastructure, equipped to handle the complexities of modern transactional ecosystems with higher precision and foresight.
AI-Driven Automation and Decision-Making in Smart Contracts
Incorporating artificial intelligence into smart contracts transforms how they perform automation and make decisions. These AI-enhanced contracts are no longer limited to executing predetermined actions; they actively interpret complex datasets, enabling dynamic, context-aware decision-making. The fusion of AI with smart contracts allows them to autonomously adapt to changing circumstances, offering unprecedented flexibility and intelligence.
AI-powered automation in smart contracts is achieved through machine learning models and advanced data processing techniques. These algorithms process and analyze large volumes of data in real-time to deliver actionable insights. For example, in financial trading platforms, AI-driven smart contracts can autonomously execute trades based on market trends, adjusting strategies as market conditions evolve, ensuring optimal outcomes without human intervention.
Moreover, decision-making within these contracts is significantly enhanced through AI’s ability to simulate “what-if” scenarios. By leveraging predictive analytics, smart contracts can foresee potential outcomes based on current data and historical performance. Consider a supply chain use case where AI-enhanced contracts optimize inventory management by predicting demand fluctuations, thus reducing storage costs and improving efficiency. These contracts can autonomously reorder supplies or reschedule shipments based on predictive models, ensuring seamless operations.
AI also empowers smart contracts with natural language processing (NLP) capabilities, enabling them to interpret and execute terms from naturally crafted legal documents. This is particularly beneficial in legal and compliance contexts, where contracts need to react and adapt to changes in regulatory frameworks or organizational policies.
Another aspect of AI-driven smart contracts is their ability to autonomously manage risks through continuous learning. Using reinforcement learning techniques, these smart contracts can gradually enhance their own performance by learning from past interactions and adapting their execution strategies. For instance, in risk-sensitive sectors like insurance, AI-driven contracts can continuously evaluate the risk profiles of clients, adjusting premiums dynamically based on evolving data, which results in more accurate and fair pricing.
By automating compliance checks and enforcement, AI-driven smart contracts can lock into evolving sets of rules and regulations. They keep abreast of legislative changes and ensure that all executed transactions are compliant, reducing the burden on human auditors and increasing trustworthiness. For industries bounded by stringent legalities, such as finance or healthcare, this offers a robust mechanism to stay compliant without manual oversight.
In conclusion, AI-enhanced automation and decision-making are revolutionizing the traditional roles of smart contracts. The ability to autonomously analyze, predict, and adjust in real-time not only increases efficiency but also opens new avenues for innovation in blockchain applications across multiple industries. These intelligent contracts mark a crucial development toward truly autonomous digital ecosystems, capable of adapting to an unpredictable world with a high degree of precision and decisiveness.
Security Enhancements in Smart Contracts Through AI Integration
Security is a paramount concern in the realm of smart contracts, and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) offers significant advancements in this area. AI in smart contracts enhances security by enabling proactive, intelligent monitoring and adaptive responses to potential threats.
AI algorithms, specifically machine learning and deep learning models, are instrumental in detecting suspicious activities and anomalous patterns that could indicate security breaches or potential exploits within the blockchain ecosystem. These models are trained on extensive datasets, allowing them to recognize deviations from normal behavior. For instance, by analyzing transaction patterns, AI systems can identify unusual activities, such as a surge in attempts to access smart contracts from unknown or suspicious IP addresses, and alert stakeholders in real-time.
Another pivotal contribution of AI is its ability to perform dynamic risk assessment. Traditional smart contracts operate on static rules, failing to adapt to evolving security threats. AI can overcome this limitation by continuously learning from new data. Consider a scenario in financial services where AI-enhanced smart contracts adjust security protocols based on current threat landscapes, addressing vulnerabilities like phishing attacks or unauthorized data access. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining the integrity of transactions in the face of constantly evolving cyber threats.
AI also plays a crucial role in predictive maintenance of smart contracts. By employing predictive analytics, AI can foresee potential issues before they manifest as security threats. For example, in a supply chain application, AI can monitor all smart contracts for signs of potential weaknesses due to outdated code versions or environmental changes in the blockchain, facilitating timely updates and patches that prevent exploitation.
The integration of AI enhances the scalability of security measures. With the increasing complexity and size of blockchain networks, AI-driven systems can handle a high volume of transactions and contract instances, ensuring robust and comprehensive security coverage without reliance on human oversight. This is especially pertinent in large-scale enterprises where manual monitoring is neither feasible nor efficient.
Moreover, AI can assist in formal verification of smart contracts, a process that ensures the correctness of contract algorithms. Machine learning models can automate this traditionally complex and labor-intensive process, providing mathematical proofs that a contract will execute as intended under all possible conditions. This reduces the likelihood of bugs and vulnerabilities in smart contracts, with AI systems performing continuous audits and validations.
Finally, natural language processing (NLP) capabilities enable AI to bridge the gap between human-readable terms and machine-executable code. By understanding the language of contracts, AI can ensure that the terms encoded in smart contracts accurately reflect the intentions and agreements of the involved parties, thereby minimizing the risk of misinterpretations or coding errors which could be exploited by malicious actors.
Incorporating AI into smart contracts not only boosts their security but also builds an adaptive, vigilant system capable of defending itself against both known and emerging threats, thus paving the way for more secure blockchain ecosystems.
Real-World Applications of AI-Enhanced Smart Contracts
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly broadened the horizons of smart contracts by introducing advanced capabilities that address real-world challenges across multiple sectors. Here’s a deep dive into several impactful applications:
In the financial sector, AI-enhanced smart contracts are transforming processes like insurance management, credit scoring, and trading. AI algorithms embed predictive analytics within smart contracts, allowing for dynamic adjustments based on risk assessments and market conditions. For instance, an AI-driven insurance contract can autonomously determine premium adjustments by continuously analyzing policyholder data and external factors like extreme weather predictions, making insurance solutions more relevant and personalized.
Supply chain management leverages AI-enhanced smart contracts to improve efficiency and transparency. These contracts utilize AI for real-time monitoring, enabling automated responses to logistical variables such as shipment delays or inventory shortages. By integrating IoT devices, AI analyses can track the condition and location of goods throughout the journey, updating contracts automatically, to optimize supply chain operations. This results in reduced costs and improved deliverability, as seen in how some logistics companies use these technologies to manage extensive networks with minimal manual intervention.
In healthcare, AI-enhanced smart contracts facilitate secure and compliant data sharing amongst multiple actors, such as hospitals, insurance companies, and patients. By employing natural language processing (NLP), these smart contracts translate complex regulatory documents into machine-readable code, ensuring adherence to legal standards. Consider a scenario where a patient’s treatment evolves; AI-driven contracts could update billing and insurance claims automatically based on real-time data integration from EHR systems, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
AI’s role in legal services through smart contracts is revolutionizing how contracts are drafted, managed, and executed. Legal practitioners utilize AI to automate due diligence and contract drafting by analyzing vast legal databases, ensuring comprehensive compliance checks. This type of AI application in smart compact development allows for automated identification and correction of discrepancies, ensuring faster and error-free legal processes.
The energy sector also benefits greatly from AI-enhanced smart contracts, notably in managing production, distribution, and consumption of resources. AI models can forecast energy demand and adjust supply contracts accordingly. For example, smart grids utilize these contracts to automate energy distribution, reducing costs and optimizing resource use based on instantaneous demand predictions.
Furthermore, in the realm of creative industries, AI-enhanced smart contracts streamline licensing and royalty management for digital content. Artists and creators can ensure fair compensation through contracts that use AI to monitor and log usage rights, performing real-time royalty calculations and disbursements. This is highly effective in the digital streaming market, where content consumption can now be tracked accurately day-to-day or even hour-to-hour.
Incorporating AI into smart contracts technological frameworks has proven instrumental in expanding their applicability, reliability, and adaptability. By enabling smart contracts to process complex data inputs and adjust dynamically to changing circumstances, AI facilitates innovative solutions that meet the intricate demands of various industries, driving a new era of efficiency and precision in automated processes.