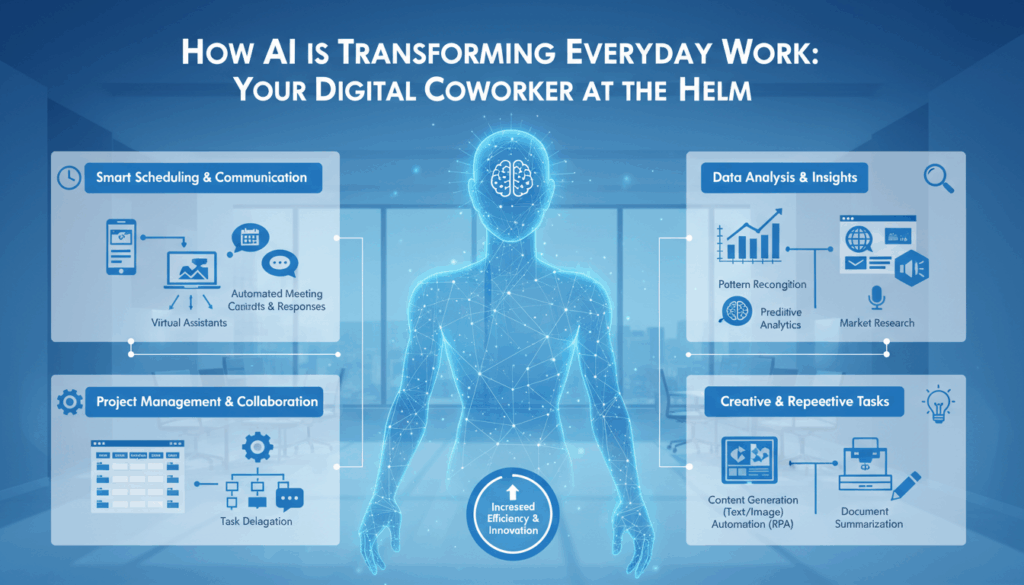
Introduction to AI in the Workplace
Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the landscape of modern workplaces, introducing automation, improving decision-making processes, and enabling innovation across various sectors. As AI technologies become increasingly sophisticated, they offer businesses opportunities to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and create new business models.
One of the most impactful aspects of AI in the workplace is its ability to handle large datasets through machine learning algorithms. These algorithms can identify patterns and trends more efficiently than human analysts, leading to faster and more accurate decision-making processes. For example, AI-powered analytics tools allow marketing departments to gain deeper insights into consumer behavior, enabling more personalized and effective marketing strategies.
In addition to decision support, AI is revolutionizing administrative tasks by automating routine processes. Digital assistants such as chatbots have become prevalent in customer service, reducing the need for human intervention in handling basic inquiries. This allows human employees to focus on more complex tasks requiring critical thinking and creativity.
Moreover, AI-driven tools are enhancing employee experience within organizations. Natural language processing (NLP) systems streamline communication across different languages, fostering a more inclusive and collaborative environment. They also assist in managing workflows by prioritizing tasks and setting up reminders, ensuring that projects remain on track.
In manufacturing and supply chain sectors, AI has enabled significant advancements in predictive maintenance and quality control. By analyzing data collected from sensors, AI systems can foresee equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs significantly. Similarly, AI algorithms help optimize supply chain logistics by predicting demand fluctuations, thereby reducing inventory shortages or surpluses.
AI’s role in workforce management cannot be overlooked either. Tools utilizing AI can match candidates to job roles more efficiently, reducing biases that often occur in traditional recruitment processes. This use of AI ensures diversity while selecting the best talents suited to organizational needs.
Overall, the introduction of AI into the workplace optimizes efficiency and promotes a culture of innovation. Employees are empowered to focus on strategy and creativity, driving companies towards a digital transformation that is both sustainable and scalable. As technology evolves, businesses will continue to integrate AI solutions, paving the way for workplaces that are smarter, more agile, and increasingly forward-thinking.
Automating Routine Tasks with AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how routine tasks are handled within businesses, driving a shift towards greater efficiency and productivity. AI enables the automation of repetitive and time-consuming tasks, thereby freeing human employees to focus on strategic initiatives and creative problem-solving.
At the core of this transformation is the application of machine learning and neural networks that can be trained to execute tasks traditionally performed by humans. For instance, consider the use of AI in data entry. Machine learning algorithms can extract relevant information from various document formats, such as invoices or reports, and input this data into a company’s database with high accuracy. This automation not only reduces errors commonly associated with manual data entry but also significantly speeds up the process.
Another area where AI showcases its capability is in email management and customer service. AI-driven email filtering tools employ algorithms to prioritize emails based on urgency and relevance, allowing employees to focus on critical communications. Additionally, intelligent chatbots are increasingly deployed to manage customer interactions. These AI systems use natural language processing (NLP) to understand and respond to customer queries in real-time, providing immediate assistance and resolving common issues without human intervention.
Scheduling and calendar management are other areas where AI has proven exceptionally useful. Tools like AI-powered virtual assistants can schedule meetings by processing the availability and preferences of attendees. For example, Google’s AI-driven assistant can suggest meeting times, send invitations, and even book conference rooms autonomously. This functionality is particularly advantageous in large organizations where scheduling can become cumbersome and time-consuming.
AI-driven process automation tools, such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), are extensively adopted for automating workflows across different business functions. RPA bots can mimic human actions, such as logging into applications, moving files, and copying data between formats, enabling businesses to streamline operations and reduce the need for human involvement in repetitive tasks. In accounting, RPA can be employed to automate reconciliations, process transactions, and manage ledgers, thereby increasing accuracy and reducing the potential for human error.
In the HR domain, AI systems enhance recruitment by automating the screening of resumes. These systems utilize algorithms to analyze applications against job descriptions, highlighting the most suitable candidates. This process not only accelerates the hiring cycle but also mitigates unconscious bias, helping organizations maintain diversity in their hiring practices.
Moreover, AI’s role extends to performance monitoring and optimization of daily tasks. By analyzing employee activity data, AI systems can provide insights into productivity bottlenecks and suggest improvements, ensuring that enterprises utilize their human resources most effectively.
The adoption of AI-driven automation is a paradigm shift towards smarter workflow management and resource utilization. Businesses implementing these technologies are poised to reap substantial benefits in terms of operational efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced employee satisfaction. As AI technology continues to evolve, its potential to innovate routine task automation promises an even more seamless and productive future for organizations worldwide.
Enhancing Decision-Making Through AI
In the modern business world, AI is setting a new benchmark in decision-making capabilities, drastically changing how organizations operate and thrive. The integration of AI into decision-support systems allows companies to leverage data more effectively, resulting in informed and timely decisions that drive success.
AI enhances decision-making by deploying sophisticated algorithms that can process huge volumes of data at high speeds. This is particularly useful in environments where traditional data analysis is impractical due to scale or complexity. Machine learning models can swiftly analyze trends and patterns, providing actionable insights that might be missed by human analysts. For instance, in the financial sector, AI systems analyze market trends and historical data to predict stock movements and identify investment opportunities, empowering financial analysts to make data-driven decisions.
An exemplary application of AI in decision-making is predictive analytics. This involves using historical data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to predict future outcomes. This approach is revolutionizing industries such as healthcare, where predictive analytics tools help diagnose health conditions early, forecast patient admissions, and plan resource allocation efficiently. By anticipating these needs, healthcare providers can enhance patient care and optimize operational efficiency.
In retail, AI-driven recommendation systems improve decision-making concerning inventory management and personalized marketing. Companies like Amazon utilize AI to study customer behavior and purchasing history, generating product recommendations that align closely with customers’ preferences. This not only boosts sales but also enhances customer satisfaction by providing a personalized shopping experience.
Risk management is another area where AI significantly bolsters decision-making. AI algorithms predict and mitigate risks by assessing variables and potential outcomes, essential for sectors like insurance and finance, where risk assessment is critical. For example, AI systems can evaluate credit applications by analyzing vast datasets including credit history, social behavior, and economic indicators, making the decision process swift and informed, thereby reducing the risk of bad loans.
AI also enhances supply chain management decisions. By analyzing data from various touchpoints in the supply chain, AI provides insights into demand forecasting, supplier reliability, and logistic bottlenecks. Companies can then adjust their operations dynamically to respond to market demands, minimize costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Moreover, AI enhances strategic decision-making by enabling scenario analysis and simulations, which are critical in business strategy development. AI systems can model different strategic scenarios to predict outcomes based on varying inputs, allowing executives to foresee the impact of their decisions and choose the best course of action.
Ethical considerations remain pivotal as AI in decision-making becomes more prevalent. It is crucial to ensure that AI systems are transparent and explainable, preventing biases and fostering trust. To this end, businesses are investing in explainable AI models that provide clarity on decision-making processes, enabling better governance and accountability.
The deployment of AI-driven decision-making tools is a game-changer that empowers organizations to scale new heights by making informed decisions quicker and with greater certainty. As these technologies continue to advance, their capacity to solve complex business challenges will expand, underscoring AI’s central role in shaping the future of intelligent decision making.
AI’s Role in Employee Development and Engagement
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a transformative force in employee development and engagement strategies, providing organizations innovative pathways to nurture talent, enhance productivity, and foster a thriving work environment. The integration of AI into human resources and team management offers opportunities to tailor employee experiences to align with both personal growth and organizational goals.
AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets allows for the personalization of employee learning and development paths. Through AI-driven learning management systems, employees receive personalized training recommendations based on their skill levels, career ambitions, and learning history. These systems use machine learning algorithms to match employees with relevant courses and resources that are most likely to enhance their skills and meet career objectives. As a result, employees are empowered to take charge of their professional development, leading to more motivated and capable workforces.
Moreover, AI-powered platforms facilitate continuous feedback loops that enhance employee engagement. These platforms can gather data from various sources such as employee surveys, performance metrics, and peer reviews, then analyze it to identify patterns and insights. For instance, predictive sentiment analysis tools can determine employee satisfaction and sentiment from open-ended feedback, enabling management to address concerns proactively and tailor engagement strategies accordingly.
Employee engagement also benefits from AI through intelligent virtual assistants and chatbots that streamline communication and support within organizations. These AI tools can assist with onboarding processes, provide instant answers to common HR queries, and offer guidance on career development pathways. By handling routine inquiries, AI frees up human resource professionals to focus on strategic initiatives and complex employee relations issues.
Another significant advantage of AI in employee development and engagement is its role in performance management. AI systems can continuously monitor and evaluate employee performance by analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and other relevant data points. These systems provide real-time feedback, allowing employees to understand their strengths and areas for improvement regularly. This approach fosters a culture of transparency and continuous improvement, guiding employees toward achieving their personal and professional goals.
AI technologies also play a crucial role in fostering an inclusive workplace environment. By utilizing natural language processing (NLP) and sentiment analysis, AI can help organizations detect biases in recruitment, promotion, and daily interactions, ensuring fair and equitable treatment for all employees. For example, AI-driven software can audit and rectify biased language in job descriptions, contributing to a more inclusive recruitment process.
Additionally, AI can enhance team collaboration through tools that enable intuitive and cross-functional workflows. These tools integrate with existing project management systems to optimize task allocations, facilitate resource sharing, and track project progress in real time. By enhancing communication and ensuring effective collaboration, AI encourages team engagement and drives productivity.
Finally, AI interventions contribute to a healthier work-life balance by identifying workload patterns and suggesting optimal work schedules. By analyzing employee productivity data, AI can recommend flexible working arrangements tailored to individual preferences while maintaining organizational efficiency.
In summary, AI aids employee development and engagement by delivering personalized learning experiences, enhancing communication, streamlining performance management, promoting inclusivity, and facilitating better work-life integration. As organizations continue to embrace AI, these technologies will play an increasingly central role in cultivating motivated, engaged, and skillful teams.
Addressing Challenges and Ethical Considerations of AI Integration
AI integration in workplaces brings about substantial transformative potential but also poses various challenges and ethical considerations that must be meticulously addressed to ensure responsible and fair implementation.
One of the primary challenges is data privacy. As AI systems require vast amounts of data to function effectively, organizations must navigate the complexities of data collection, storage, and usage. Ensuring that personal and sensitive information is handled with strict confidentiality standards is paramount. Companies must align with global data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, which mandates robust data security protocols and transparent data practices. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to legal repercussions and damage to brand reputation, underscoring the importance of adopting comprehensive data management strategies.
Another significant challenge is the issue of bias in AI algorithms. AI systems learn from existing datasets, which may unintentionally reflect or perpetuate societal biases present in those datasets. This can lead to unfair treatment of individuals based on gender, race, or socioeconomic status. For example, biased algorithms in recruitment software could inadvertently favor candidates from certain demographics over others. To mitigate such risks, developers are increasingly focusing on creating explainable AI (XAI) models, which allow users to understand and trust the decision-making processes of AI systems. Incorporating fairness assessments during the development phase and conducting regular audits of AI tools are crucial steps towards minimizing algorithmic bias and promoting ethical AI.
Ethical considerations also extend to the impact of AI on employment. While AI automation can enhance productivity, it can simultaneously threaten jobs traditionally held by humans, leading to workforce displacement. Businesses must be proactive in formulating strategies that manage this transition, which might involve reskilling and upskilling employees to prepare them for roles that require more complex problem-solving abilities or creativity—areas where human intelligence surpasses AI capability. By investing in continuous learning programs, organizations not only empower their workforce but also mitigate the societal impact of job displacement.
Transparency and accountability in AI systems are critical to fostering trust among users. Organizations need to ensure that their AI systems are not only effective but also operate transparently. This involves documenting AI decision-making processes and maintaining open channels of communication about how AI tools are integrated into business functions. Establishing clear accountability frameworks is necessary to address instances where AI systems malfunction or produce undesirable outcomes.
Finally, AI is associated with significant ethical concerns regarding surveillance and autonomy. For instance, companies using AI for employee monitoring should balance productivity benefits with the preservation of individual privacy and autonomy. Implementing AI policies that respect workers’ rights and freedoms is essential to maintaining a respectful and ethical workplace environment.
Adopting an ethical approach to AI integration involves multi-layered strategies that encompass technology design, regulatory compliance, and human-centric considerations. Organizations must remain vigilant and proactive as they integrate AI into their operations, ensuring that these systems are inclusive, fair, and geared towards genuine improvements in business processes and societal welfare.