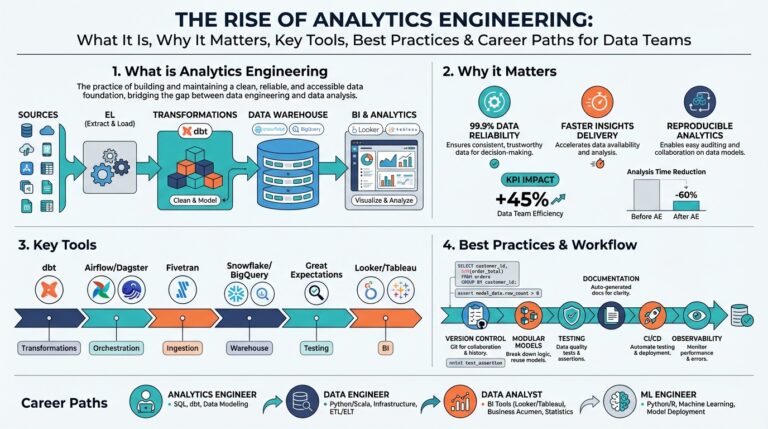
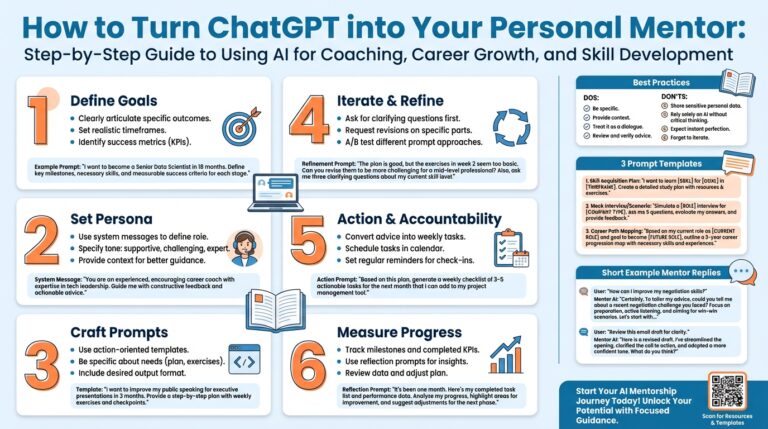
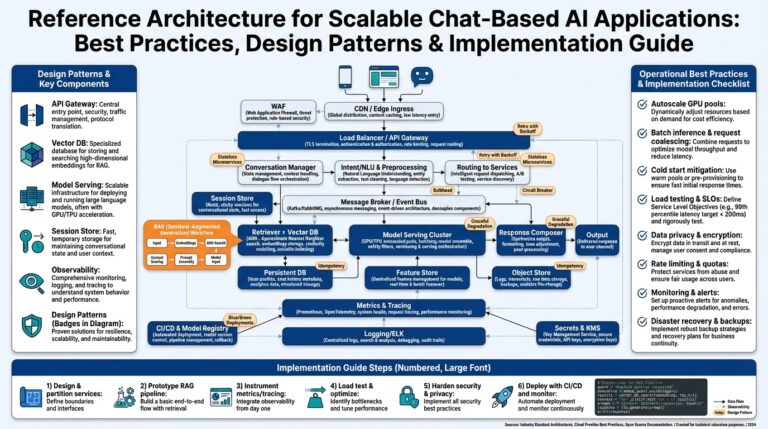
The Titan Breakthrough is rapidly gaining attention as a transformative concept across multiple industries, from engineering and technology to business innovation. But what does this breakthrough truly entail, and why is it generating so much buzz? In this post, we’ll walk you through the essentials of the Titan Breakthrough, breaking down its key principles, steps for adoption, and real-world examples.
What is the Titan Breakthrough?
The term “Titan Breakthrough” refers to a significant leap in technology or processes that enables exponential growth or improvement in a field. Unlike incremental changes, a breakthrough of this scale often redefines standards, pushes boundaries, and disrupts status quos.
Why Is It Important?
The impact of such breakthroughs can be seen historically: from the industrial revolution to the internet age, leaps in innovation have transformed economies and the very structure of society. According to McKinsey’s Technology Trends, embracing breakthrough technology can increase efficiency, foster competitiveness, and enhance adaptability in rapidly changing markets.
Core Principles Behind the Titan Breakthrough
- Innovation-driven: The core focus is on developing new solutions rather than improving existing ones.
- Scalability: Solutions are designed to impact not just a team or division, but entire organizations or industries.
- Disruption: Old models and processes are reimagined or rendered obsolete.
- Agility: Nimble adaptation to feedback and rapid iteration are essential.
How to Implement the Titan Breakthrough: Step-by-Step
- Identify the Core Problem: Pinpoint a major challenge or inefficiency that requires radical change. For example, energy companies identified battery storage as crucial for renewable energy adoption.
- Encourage Disruptive Thinking: Foster a culture that rewards out-of-the-box ideas. Organizations like MIT and Stanford University have innovation labs dedicated to this.
- Leverage Cross-Disciplinary Teams: Bring together experts from various backgrounds to address problems from different angles. According to Harvard Business Review, this approach increases the likelihood of discovering novel solutions.
- Prototype Rapidly: Build quick, testable models to validate ideas before large-scale investment. Tech giants like Google are known for their rapid prototyping approaches.
- Iterate and Scale: Refine successful prototypes, gather feedback, and prepare for wide-scale deployment.
Examples of the Titan Breakthrough
- Tesla’s Battery Technology: Tesla’s advancements in lithium-ion battery technology have fundamentally changed electric mobility worldwide. Read more about this on Scientific American.
- CRISPR Gene Editing: The ability to precisely edit genes has huge implications for medicine, agriculture, and beyond. Explore the science at Nature.
- Cloud Computing: The shift to on-demand, scalable cloud services has transformed the IT landscape. For more, see Google’s cloud computing overview.
Challenges and Considerations
While the Titan Breakthrough promises substantial rewards, there are hurdles to consider:
- Risk of Failure: High-reward innovations come with greater risk. Not every radical idea succeeds.
- Resistance to Change: Both organizational inertia and regulatory hurdles can slow adoption. Explore strategies to overcome this at Harvard Business Review.
- Resource Allocation: Balancing daily operations with breakthrough projects is challenging.
Conclusion
The Titan Breakthrough represents a powerhouse of change capable of drastically reshaping industries. By understanding its principles, following proven steps, and learning from successful case studies, you too can position yourself or your organization at the forefront of innovation. For further insights, consider exploring reports from Deloitte or taking online courses through edX.