Introduction to Voice AI: Beyond ChatGPT
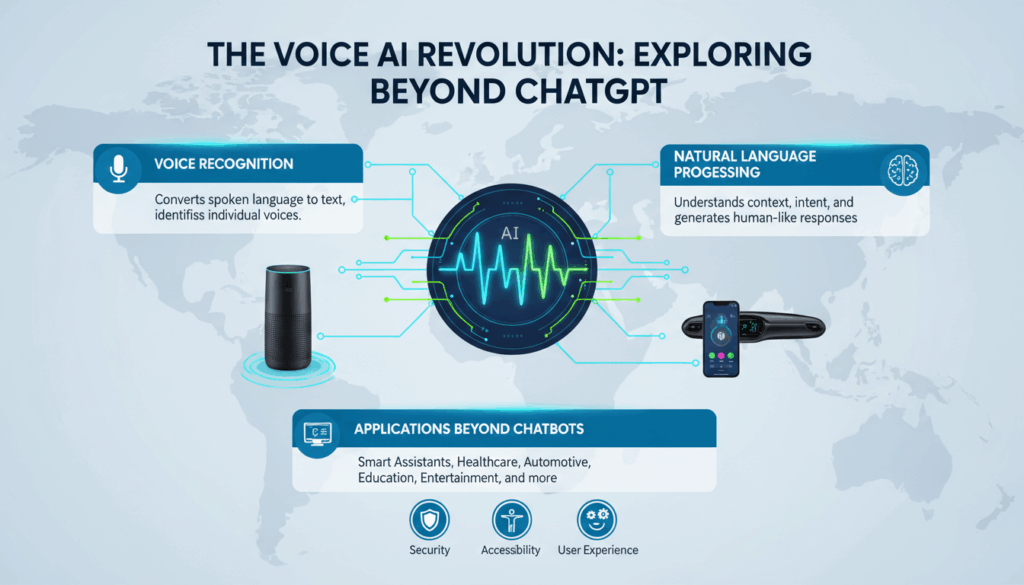
Voice AI, a rapidly advancing field in artificial intelligence, extends the capabilities of conversational systems beyond text-based interactions like ChatGPT. While text-based AI, such as ChatGPT, has demonstrated remarkable proficiency in understanding and generating human language in written form, voice AI introduces a new dimension by enabling machines to interpret and respond to spoken language. This technology harnesses both natural language processing (NLP) and speech recognition to facilitate seamless vocal communication between humans and machines.
The essence of voice AI lies in its ability to transform spoken words into text, process the text to derive meaning, and then convert the generated response back into speech. This involves sophisticated components such as automatic speech recognition (ASR), which translates spoken words into text, and text-to-speech (TTS) systems, which synthesize written text into audible speech. Let’s delve deeper into these components to understand how voice AI functions.
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): At the core of voice AI, ASR systems rely on statistical models and neural networks to interpret spoken language. The process begins with the conversion of voice signals into a digital format, breaking it down into segments that algorithms can analyze. Advanced models such as deep neural networks (DNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are often employed to recognize patterns and deduce phonetics, enabling the system to accurately transcribe speech even in noisy environments or with diverse accents.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Once speech is transcribed into text, the system must comprehend the text’s intent. This stage involves natural language understanding, where AI models assess context, semantics, and syntax to determine what the user intends to convey. Machine learning techniques, including transformer models, are pivotal in parsing the meaning of the text. These models are trained on vast datasets, learning to discern nuances and ambiguities with human-like precision.
Text-to-Speech (TTS) Synthesis: After processing and formulating an appropriate response, voice AI systems must deliver this response vocally. TTS technology comes into play here, utilizing sophisticated algorithms to convert text into natural-sounding speech. Cutting-edge TTS models, often based on neural networks, are capable of generating speech with varied intonation, emotion, and rhythm, making interactions feel more authentic and engaging.
Applications and Use Cases: The integration of voice AI into consumer and enterprise applications is endless. Personal assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri exemplify its widespread appeal, powering everyday devices from smartphones to smart home gadgets. In the business world, voice AI is revolutionizing customer service by enabling intelligent virtual agents that handle inquiries efficiently. Moreover, industries such as healthcare leverage voice AI for tasks like voice-driven data entry and patient interaction, enhancing both efficiency and accessibility.
Technical Challenges and Innovations: Despite its potential, voice AI presents several challenges. Accurately understanding diverse accents, managing noise interference, and handling speaker idiosyncrasies are persistent hurdles. Innovations such as adaptive learning algorithms and multi-lingual training continue to enhance accuracy and resilience. Research in voice cloning and emotion recognition further aims to make interactions even more personalized and context-aware.
Voice AI continues to evolve rapidly, offering a promising pathway for the next generation of human-machine interaction. As this technology matures, it promises to make digital interactions more inclusive, engaging, and intuitive, reshaping how we connect with the digital world.
Emerging Voice AI Technologies and Their Applications
Voice AI technologies are rapidly evolving, introducing groundbreaking innovations that expand their capabilities and applications across various domains. These emerging technologies not only enhance voice recognition precision but also facilitate more personalized and context-aware interactions between humans and machines.
One of the key advancements is the development of transformers in speech processing. Transformers, initially popularized by models like GPT for text, are now being adapted to improve automatic speech recognition (ASR) and natural language processing (NLP) for voice AI. By leveraging attention mechanisms, transformers can focus on relevant parts of an audio signal, enabling superior performance in recognizing speech in challenging environments such as noisy or multi-speaking scenarios. This enhancement significantly improves the ability of devices to understand speech accurately, regardless of background interference, thus broadening their usability.
Moreover, transfer learning has emerged as a pivotal technique within voice AI. By training models on vast, diverse datasets, and subsequently refining them for specific tasks, transfer learning allows systems to adapt more efficiently to particular languages, accents, or domain-specific vocabulary. This adaptability is crucial for developing robust voice AI solutions that cater to global and multicultural audiences. For example, a voice assistant could effortlessly switch between languages or dialects in real-time, catering to multilingual households or businesses.
Another innovation reshaping voice AI is voice cloning, a sophisticated method leveraging deep learning to replicate human voices with high accuracy. This technology has transformative potential in entertainment and content creation, allowing for personalized audio experiences that resonate with individual user preferences based on synthesized voices of their favorite celebrities or recognizable characters. Similarly, in accessibility, voice cloning can replicate a person’s voice, providing a significant resource for those who lose speech due to medical conditions, enabling them to communicate more effectively using a digital proxy of their own voice.
Voice AI applications are extending into healthcare, where voice-enabled diagnostic tools analyze patients’ speech patterns to detect conditions like depression, stress, or even certain neurological disorders. By identifying subtle changes in voice frequency and patterns, these tools can offer early indicators of health issues, facilitating timely intervention and monitoring.
In retail, emerging voice AI technologies are reshaping customer service with systems that understand complex human emotions and sentiments, providing empathetic responses tailored to customer tone and mood. These emotional awareness features lead to more satisfying and productive customer interactions, strengthening brand loyalty and enhancing user experience.
In educational settings, voice AI is revolutionizing learning environments by offering interactive and personalized tutoring experiences. By recognizing student responses in real-time and adapting content delivery based on student needs and comprehension levels, voice AI tools can provide more effective and engaging educational interactions.
These applications illustrate the transformative potential of emerging voice AI technologies. As these innovations continue to advance, they promise to break barriers of communication and understanding, fostering a more interconnected world where voice-driven interactions are seamless and intuitive.
Integrating Voice AI into Daily Life: Practical Use Cases
Voice AI is progressively embedding itself into various facets of everyday life, transforming how we interact with technology by making it more intuitive and accessible. Practical use cases for integrating Voice AI are numerous, and they can significantly enhance convenience and efficiency in daily routines.
In domestic environments, Voice AI powers smart home systems, enabling seamless voice control over household devices. Imagine setting your morning routine with a simple voice command: “Good morning.” Instantly, your smart assistant could open the blinds, start your coffee maker, adjust the thermostat, and play your favorite news podcast, all while you prepare for the day. The capability to control lighting, security systems, and even kitchen appliances via voice commands offers not only convenience but also assists those with mobility challenges, making homes truly smart and accessible.
Voice AI’s impact on commuting is equally transformative. In cars, voice assistants enable hands-free operations, allowing drivers to answer calls, dictate messages, set navigation routes, and adjust the media playing—all without taking their eyes off the road or hands off the wheel. This promotes safer driving experiences. Moreover, entertainment systems in vehicles are becoming increasingly voice-integrated, allowing passengers to easily search for music, podcasts, or control other multimedia features, enhancing the travel experience.
In professional settings, Voice AI accelerates productivity by streamlining tasks such as scheduling meetings, sending emails, and managing to-do lists. Virtual assistants can handle these administrative details, leaving workers free to focus on more complex tasks. In conference rooms, Voice AI can transcribe meetings in real time, providing detailed notes automatically and ensuring that no critical information is lost. These applications not only save time but also increase workplace efficiency and reduce the cognitive load on employees.
Voice AI finds significant application in the realm of online commerce as well. Retailers are adopting voice-activated systems to enhance customer service, guiding users through product inquiries, purchases, and support services. Online shoppers can now check product details, availability, and even order items using voice commands. This provides a hands-free shopping experience, tapping into the convenience sought by digital consumers.
Health and wellness sectors also benefit substantially from Voice AI technology. At home, individuals use voice-activated fitness trackers to receive custom workout suggestions, monitor health metrics, or even engage in guided meditation practices. In a more clinical context, voice-based tools facilitate symptom checking, medication reminders, and even remote patient monitoring. Healthcare providers can focus on patient care rather than administrative duties, and patients enjoy more personalized and timely health management.
Educational environments are increasingly adopting Voice AI to create personalized and adaptive learning experiences. Through voice interactions, educational platforms can offer dynamic learning modules to students, responding to their verbal cues and adjusting the difficulty level or subject matter according to the student’s pace and understanding. This fosters a more engaging and customized learning atmosphere, catering to diverse learner needs.
By weaving Voice AI into the fabric of daily activities, these practical use cases demonstrate the versatility and potential of this technology. As voice AI continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly become an indispensable tool in enhancing the quality, accessibility, and efficiency of our daily lives. Through fostering more natural interactions with technology, Voice AI is poised to become a cornerstone of the modern digital ecosystem.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges in Voice AI Development
Voice AI technology is rapidly advancing, presenting transformative opportunities in various fields, yet it simultaneously raises significant ethical considerations and challenges. Developing responsible voice AI systems necessitates a careful examination of issues such as privacy, bias, accessibility, and security.
Privacy concerns emerge as voice AI systems consistently collect and analyze vast amounts of audio data, often including sensitive information. As these systems become more integrated into personal and professional spaces, ensuring that user data is securely managed and stored is paramount. Developers must implement robust encryption and anonymization techniques to protect user data from unauthorized access or breaches. Transparency about data usage and securing informed user consent are crucial steps to maintain trust.
Bias in voice AI systems is another critical ethical challenge. These systems rely heavily on vast datasets to learn and make decisions. If these datasets are not diverse, the AI might develop a bias towards certain accents, languages, or demographics. For instance, a voice assistant trained predominantly on English speakers from a specific region may struggle with users who have different accents, leading to inaccuracies and potential discrimination. Developers should ensure that training datasets are diverse and representative of the global population. Implementing regular audits and adjustments to the models can help mitigate bias over time.
Accessibility is a vital consideration in making voice AI inclusive of all users, including those with disabilities. Voice AI technology holds the promise of increasing accessibility for people with visual impairments or those who struggle with traditional text-based communication methods. However, designing systems that can effectively recognize and respond to non-standard speech patterns or speech impairments is a challenge that developers must address. Collaborating with experts in accessibility and users with diverse needs can lead to more inclusive and effective solutions.
Security challenges are intrinsically tied to voice AI systems due to their dependence on always-listening devices and cloud-based processing. Unauthorized access to voice-assisted devices can compromise not only user privacy but also security, as these systems often control smart home devices and access sensitive information. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as voice biometrics alongside traditional security protocols, can help mitigate these risks.
In the development of voice AI, ethical and regulatory considerations must go hand in hand with technological advancement. Governments and regulatory bodies need to establish clear guidelines and frameworks that hold developers accountable and ensure that voice AI technologies are deployed responsibly. Global discussions among policymakers, technologists, and ethicists can foster the creation of standards that prioritize ethical considerations while encouraging innovation.
By addressing these ethical challenges, developers can build voice AI systems that not only push the boundaries of technology but also contribute positively to society, ensuring a more equitable and trustworthy digital future for all users.
Future Trends in Voice AI: What’s Next?
As voice AI technology continues to evolve rapidly, several emerging trends are poised to redefine its landscape. One significant development is the increased integration of multimodal interfaces, where voice AI is combined with other forms of interaction such as visual and tactile inputs. This fusion allows for more enriching user experiences by providing contextual data through screens or haptic feedback alongside voice commands. For example, smart assistants could overlay visual cues on augmented reality (AR) glasses while you speak, offering real-time translations or navigation details.
Another exciting trend is the advancement of emotional AI, which seeks to make voice interactions more empathetic and responsive to the user’s emotional state. Leveraging sophisticated algorithms, these systems will be capable of detecting nuances such as tone, pitch, and inflection to determine the user’s mood, then adjust responses accordingly. This capability could transform customer service experiences, enabling virtual agents to provide support that feels genuinely personalized and understanding.
Moreover, the rising focus on edge computing will significantly influence voice AI capabilities. Traditionally dependent on cloud processing, voice AI systems face latency and privacy issues due to data being sent and processed remotely. With edge computing, processing can occur locally on the device, reducing response times and enhancing data privacy. This shift is particularly valuable for mobile and IoT devices, which require rapid and secure voice interactions without reliance on constant internet connectivity.
Privacy-centric design is also becoming a key focus for future voice AI developments. Consumers are increasingly concerned about data privacy, prompting companies to prioritize user control over data collection and storage. Innovations in differential privacy and federated learning are being integrated into voice AI systems to ensure user data remains confidential while still being used to improve AI accuracy and functionality.
On the horizon, personalized voice assistants tailored to individual user needs and preferences are expected to become the norm. These advanced systems will learn from individual user interactions and behaviors to offer more relevant and customized services. A digital assistant could, for instance, learn a user’s daily schedule and preferences over time to preemptively provide reminders or suggest optimal routes for a commute based on live traffic updates.
The expansion of voice AI in multilingual and multicultural contexts is another burgeoning area. Advances in neural machine translation are allowing voice assistants to fluently and accurately switch between languages in real-time, catering to increasingly globalized and diverse user bases. This capability enhances voice AI’s utility in international business meetings or travel, where seamless cross-lingual communication is essential.
Lastly, the integration of blockchain technology with voice AI presents future possibilities, particularly in securing transactions facilitated by voice interactions. Blockchain can add an unprecedented level of security and trustworthiness to transactions, crucial for applications involving sensitive data, such as banking and healthcare.
These trends indicate a dynamic future for voice AI, characterized by deeper integration into daily life, heightened personalization, and enhanced security. As these technologies evolve, they are set to revolutionize how humans interact with machines, forging a more intuitive and responsive digital ecosystem.